Electroacupuncture preconditioning alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus- interposed nucleus nerve pathway
- PMID: 35610007
- PMCID: PMC9924790
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.03.005
Electroacupuncture preconditioning alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus- interposed nucleus nerve pathway
Abstract
Objective: To explore whether the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) participates in regulation of the anti-myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) effect of electroacupuncture (EA) and whether this is achieved through the PVN-interposed nucleus (IN) neural pathway.
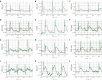
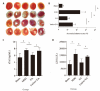
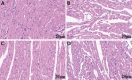
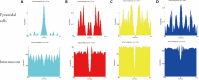
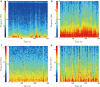
Methods: The modeling method of myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury was achieved by ligating the left anterior descending coronary artery in Sprague-Dawley rats. We used the Powerlab multi-channel physiological recorder system to record electro-cardiograms and analyze the changes in ST segment displacement; 2,3,5-Triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining was used to observe the percentage of myocardial infarction areas. Detecting cardiac troponin I (cTnI), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in serum was done with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. Morphological changes in the myocardium were detected in each group with hematoxylin-eosin staining of paraffin sections. Detection of c-fos protein expression in the PVN of the hypothalamus was done with the immune-ofluorescence method. The Plexon multi-channel acquisition system recorded PVN neuron discharges and local field potentials in each group of rats. Offline Sorter software was used for cluster analysis. Neuro Explorer software was used to perform autocorrelation, raster and frequency characteristics and spectral energy analysis of neuron signals in each group.
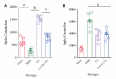
Results: Compared with the MIRI model group, the areas of myocardial infarction in the EA group were significantly reduced; the expression of cTnI, LDH in serum was decreased significantly. The firing frequency of pyramidal cells in the PVN was significantly increased and the spectrum energy map showed energy was reduced, c-fos expression in PVN was reduced, this indicated that neuronal activity in the PVN participates in the effect of EA improving myocardial injury. In addition, we used the kainic acid method to lesion the IN and observed that the effect of EA was weakened. For example, the area of myocardial infarction of lesion IN + EA group in rats was significantly increased compared with that resulting from EA group, the expression of cTnI, LDH in serum was significantly increased, the firing frequency of pyramidal cells in the PVN was significantly reduced. A spectral energy diagram shows that the energy after damage was higher than that of EA group. At the same time, the expression of c-fos in the PVN increased again.
Conclusion: Our results indicated that the PVN-IN nerve pathway may participate as an effective pathway of EA to improve the effect of myocardial injury.
Keywords: L-lactate dehydrogenase; acupuncture; interposed nucleus; myocardial reperfusion injury; paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus; troponin I.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons projecting to the rostral ventrolateral medulla.Eur J Neurosci. 2024 Sep;60(5):4861-4876. doi: 10.1111/ejn.16480. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Eur J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39054660
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture preconditioning on neuronal activities in lateral hypothalamus area of myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Aug 25;46(8):671-8. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.201176. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34472752 Chinese.
-
[Effects of electroacupuncture pretreatment on GABAA receptor of fastigial nucleus and sympathetic nerve activity in rats with myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2023 Jun 12;43(6):669-78. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20221203-k0003. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37313561 Chinese.
-
[Effect of Electroacupuncture at "Shenmen" (HT 7)- "Tongli" (HT 5) of Heart Meridian on Neuronal Activities in Paraventricular Nucleus of Hypothalamus in Myocardial Ischemia Rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018 Jul 25;43(7):406-13. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.180144. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018. PMID: 30094975 Chinese.
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture preconditioning on the contents of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in lateral hypothalamus area and cerebellar fastigial nucleus of rats with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2021 May 12;41(5):525-30. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20200509-k0001. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34002567 Chinese.
Cited by
-
[Mechanisms by Which Paraventricular Hypothalamic Nucleus Participates in the Acupuncture Treatment of Diseases].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 Jan 20;56(1):26-34. doi: 10.12182/20250160202. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40109474 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Key targets of signal transduction neural mechanisms in acupuncture treatment of cardiovascular diseases: Hypothalamus and autonomic nervous system.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 20;10(19):e38197. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38197. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39386880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electroacupuncture pretreatment mediates sympathetic nerves to alleviate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via CRH neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus.Chin Med. 2024 Mar 6;19(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00916-y. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38448912 Free PMC article.
-
Neuro- and immuno-modulation mediated by the cardiac sympathetic nerve: a novel insight into the anti-ischemic efficacy of acupuncture.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Oct;44(5):1058-1066. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240423.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39380238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of mechanism of electroacupuncture pretreatment for prevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Oct;30(10):e14920. doi: 10.1111/cns.14920. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39361504 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hao F, Cai RL, Yu Q, et al.. Effect of electroacupuncture preconditioning on the expressions of NF-κB p65, IκBα and IKKβ in myocardial tissue of the rats with acute myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2020; 40:1103-7. - PubMed
-
- Yang L, Yang J, Wang Q, et al.. Cardioprotective effects of electroacupuncture pretreatment on patients undergoing heart valve replacement surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Thorac Surg 2010; 89:781-6. - PubMed
-
- Jang I, Cho K, Moon S, et al.. A study on the central neural pathway of the heart, Nei-Kuan (EH-6) and Shen-Men (He-7) with neural tracer in rats. Am J Chin Med 2003; 31:591-609. - PubMed
-
- Chi HJ, Chen ML, Yang XC, et al.. Progress in therapies for myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Curr Drug Targets 2017; 18:1712-21. - PubMed
-
- Zhong MK, Duan YC, Chen AD, et al.. Paraventricular nucleus is involved in the central pathway of cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats. Exp Physiol 2008; 93:746-53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
