Effectiveness of Zhuling decoction on diuretic resistance in patients with heart failure: a randomized, controlled trial
- PMID: 35610014
- PMCID: PMC9924782
- DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220311.003
Effectiveness of Zhuling decoction on diuretic resistance in patients with heart failure: a randomized, controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: To test the effects of Zhuling decoction on patients with diuretic resistance in heart failure compared with a group of patients undergoing conventional treatment alone.
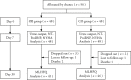
Methods: This research was a prospective, randomized, controlled study. From July 2018 to August 2020, 96 diuretic resistance patients from the Cardiovascular Research Center of Taicang Hospital affiliated with Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grade III Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine) were enrolled in the study. The subjects were randomly divided into an observation group (48 cases) and a control group (48 cases). Patients in both groups received conventional treatment. In addition, observation group patients received Traditional Chinese Medicine Zhuling decoction. The primary endpoint was the urine output mean difference between Day 1 and Day 7 after treatment. Secondary endpoints were the changes over time in the N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classification, and Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ). The safety and tolerability of the drug were comprehensively evaluated based on adverse drug reactions, as well as laboratory-assisted tests for liver and kidney function and electrolytes.
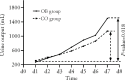
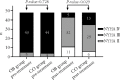
Results: Significant improvements were demonstrated for urine output in the two groups at Day 7, with a 1325 1045 mL difference in favor of the observation group ( = 0.018). The observation group also had greater improvements in NT-proBNP and NYHA functional classification changes than the control group. At the 30th day of follow-up, a significant reduction in negative findings on the MLHFQ from baseline was observed in both groups, but the observation group demonstrated a significantly greater reduction than the control group ( <0.001).
Conclusions: Zhuling decoction could be used in combination therapy for patients with diuretic resistance in heart failure in addition to standard treatment.
Keywords: Zhuling decoction; diuretic resistance; heart failure; randomized controlled trial; treatment outcome; urine output.
Figures


References
-
- Hao G, Wang X, Chen Z, et al.. Prevalence of heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction in China: the China hypertension survey, 2012-2015. Eur J Heart Fail 2019; 21:1329-37. - PubMed
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, et al.. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020; 141:e139-596. - PubMed
-
- Murphy SP, Ibrahim NE, Januzzi JL, Jr. Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a review. JAMA 2020; 324:488-504. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW, et al.. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018; 137:e67-492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
