Progress in osteoarthritis research by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- PMID: 35610209
- PMCID: PMC9130253
- DOI: 10.1038/s41413-022-00207-y
Progress in osteoarthritis research by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Abstract
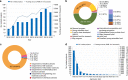
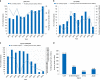
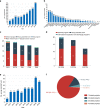
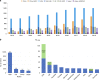
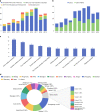
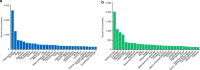
Osteoarthritis (OA) in China is gradually becoming an important scientific research area that has had a significant impact on research and development (R&D) activities in the OA field worldwide. This article summarizes the R&D progress related to OA in China in recent years. The National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) is a national funding institution for basic research and plays a critical role in promoting and supporting Chinese scholars' R&D activities. We collected and analyzed information on NSFC funding in the field of OA from 2010 to 2019, including the amount, the level and the program categories of the funded projects. The data fully demonstrate the important and positive role of the NSFC in supporting free exploration, cultivating research teams and young talent, and boosting OA R&D. In this article, we outline and discuss hot topics in focused areas, key advances in this field and the prospects for progress in OA research in China.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

