An in vivo gene amplification system for high level expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 35610221
- PMCID: PMC9130285
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30529-8
An in vivo gene amplification system for high level expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
Bottlenecks in metabolic pathways due to insufficient gene expression levels remain a significant problem for industrial bioproduction using microbial cell factories. Increasing gene dosage can overcome these bottlenecks, but current approaches suffer from numerous drawbacks. Here, we describe HapAmp, a method that uses haploinsufficiency as evolutionary force to drive in vivo gene amplification. HapAmp enables efficient, titratable, and stable integration of heterologous gene copies, delivering up to 47 copies onto the yeast genome. The method is exemplified in metabolic engineering to significantly improve production of the sesquiterpene nerolidol, the monoterpene limonene, and the tetraterpene lycopene. Limonene titre is improved by 20-fold in a single engineering step, delivering ∼1 g L-1 in the flask cultivation. We also show a significant increase in heterologous protein production in yeast. HapAmp is an efficient approach to unlock metabolic bottlenecks rapidly for development of microbial cell factories.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The University of Queensland has filed two Australian provisional patents on the methods for gene amplification to claim the intellectual property (Inventors: B.P. and C.E.V. Australian Patent Application numbers: 2022900699 and 2022901094). C.E.V. has a financial interest in Provectus Algae. Other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
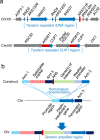

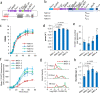



References
-
- Peng B, Williams T, Henry M, Nielsen L, Vickers C. Controlling heterologous gene expression in yeast cell factories on different carbon substrates and across the diauxic shift: a comparison of yeast promoter activities. Microb. Cell Factories. 2015;14:91. doi: 10.1186/s12934-015-0278-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

