Rheumatoid Arthritis Co-relation with Anti-CCP Antibodies with special reference to its Prevalence in Asymptomatic First-Degree Relatives
- PMID: 35611105
- PMCID: PMC9092096
- DOI: 10.31138/mjr.33.1.42
Rheumatoid Arthritis Co-relation with Anti-CCP Antibodies with special reference to its Prevalence in Asymptomatic First-Degree Relatives
Abstract
Objectives: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease. First-degree relatives (FDR) of patients with RA sharing genetic and environmental risk factors for RA may represent a pre-RA state. This study showed the clinical co-relation of RA with Anti-Cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibody and prevalence of sero-positive anti-CCP antibody in asymptomatic first-degree relatives (AFDR) of rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Methods: Total 85 RA patients, 105 AFDR, and 105 healthy controls who belonged to the same geographical area having no family history of autoimmune diseases were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. RA patients were clinically examined, and DAS-28 was calculated. Anti-CCP was sent for RA patients, AFDR, and control group. Appropriate statistical tools were applied to find if any significant co-relation exists.
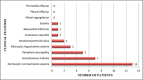
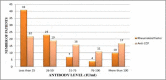
Results: DAS 28 co-related significantly with anti-CCP positivity (p≤0.01) but not with Rheumatoid Factor (RF). No significant co-relation was observed between anti-CCP and extra-articular manifestation (EAM) (p≥0.05). Seropositivity for anti-CCP antibody was detected in 22/105 (20.9%) AFDR and in 13/105 (12.3%) control group respectively. Anti-CCP antibody seropositivity was more prevalent in AFDR than in control group but the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.1378).
Conclusions: Anti-CCP should be preferred over RF as it correlated well with disease activity, but it does not guide well for the EAM. The higher sero-prevalence of Anti-CCP in AFDR may lead to higher risk of development of RA in near future. Thus, all AFDR should be screened so that we may follow up the positive cases for early detection and treatment of RA.
Keywords: anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody; asymptomatic first-degree relative; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2022 The Mediterranean Journal of Rheumatology (MJR).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Greater prevalence of seropositivity for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in unaffected first-degree relatives in multicase rheumatoid arthritis-affected families.Korean J Intern Med. 2013 Jan;28(1):45-53. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2013.28.1.45. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Korean J Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23345996 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody is highly associated with rheumatoid factor and radiological defects in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Mar;98(12):e14945. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014945. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30896663 Free PMC article.
-
Relatives without rheumatoid arthritis show reactivity to anti-citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies that are associated with arthritis-related traits: studies of the etiology of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2013 Aug;65(8):1995-2004. doi: 10.1002/art.38022. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. PMID: 23754702 Free PMC article.
-
[Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: relation with clinical features, cytokines and HLA-DRB1].Biomedica. 2004 Jun;24(2):140-52. Biomedica. 2004. PMID: 15495594 Review. Spanish.
-
[Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid arthritis].Rinsho Byori. 2010 May;58(5):466-79. Rinsho Byori. 2010. PMID: 20560456 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Investigation of periodontitis, halitosis, xerostomia, and serological characteristics of patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis and identification of new biomarkers.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 21;14(1):4316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55004-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38383594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA. Incidence and prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis, based on the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2006;36(3):182–8. - PubMed
-
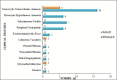
- Young A, Koduri G. Extra-articular manifestations and complications of rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res ClinRheumatol 2007;21(5):907–927. - PubMed
-
- Hazelton RA, Cross SM, Robert G, Strachan N. A family study of the prevalence of antibodies to the rheumatoid arthritis associated nuclear antigen (RANA). Br J Rheumatol 1986;25:349–352. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources