Effect of Acupuncture on the Cognitive Control Network of Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35611301
- PMCID: PMC9124489
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S356044
Effect of Acupuncture on the Cognitive Control Network of Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Abnormal central nervous system function is the key central pathological factor leading to chronic pain in patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA). Acupuncture can effectively relieve the pain of KOA patients. However, the central nervous mechanism of acupuncture treating KOA is not fully understood. This trial will use functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) analysis techniques to investigate the potential central nervous mechanism of acupuncture treatment of KOA.
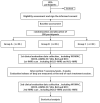
Materials and methods: A total of 108 patients will be randomized (in a 1:1:1 ratio) into three groups, this trial will include 4-week treatment, patients in groups A and B will receive 20 acupuncture and sham acupuncture sessions, respectively, patients in group C will not receive any intervention, and all patients will receive fMRI scans before and after the intervention. The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index score (WOMAC) will be the primary clinical outcome. Then, we will explore the functional changes of the cognitive control network (CCN) in the brains of KOA patients through whole brain functional connectivity (FC) analysis and seed-based functional connectivity (sFC) analysis. Pearson correlation coefficient will be used to analyze the relationship between the improved value of the clinical correlation scale and the change of fMRI data.
Discussion: This trial will analyze the efficacy of verum acupuncture, sham acupuncture and the waiting-list for KOA and explore the activity of the CCN in three groups of patients by fMRI, so as to reveal the central nervous mechanisms of acupuncture in the treatment of KOA.
Study registration: This study is approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No: 2019HL-133-01) and registered in the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR2000038554.
Keywords: acupuncture; cognitive control network; knee osteoarthritis; randomized controlled trial.
© 2022 Yin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Efficacy and Brain Network Mechanism of Acupuncture for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Study Protocol for Randomized Controlled Neuroimaging Trial.J Pain Res. 2025 Jan 23;18:391-404. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S500024. eCollection 2025. J Pain Res. 2025. PMID: 39872091 Free PMC article.
-
The cerebral mechanism of acupuncture for treating knee osteoarthritis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2019 Feb 13;20(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3233-7. Trials. 2019. PMID: 30760314 Free PMC article.
-
The long-term effect of acupuncture for patients with knee osteoarthritis: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 16;99(42):e22599. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022599. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33080693 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Acupuncture-Related Therapy in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Pain Res. 2021 Jul 19;14:2209-2228. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S315956. eCollection 2021. J Pain Res. 2021. PMID: 34321920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with acupuncture combined with Chinese herbal medicine: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Nov;10(11):11430-11444. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2565. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34872268
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources