General population normative scores for interpreting the BODY-Q
- PMID: 35611607
- PMCID: PMC9541838
- DOI: 10.1111/cob.12528
General population normative scores for interpreting the BODY-Q
Abstract
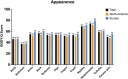
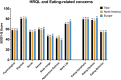
The BODY-Q is a patient-reported outcome measure used to assess outcomes in patients undergoing weight loss and/or body contouring surgery (BC) following massive weight loss. Normative values for the BODY-Q are needed to improve data interpretation and enable comparison. Thus, the aim of this study was to determine normative values for the BODY-Q. Participants were recruited internationally through two crowdsourcing platforms. The participants were invited to complete the BODY-Q scales through an URL link provided within the crowdsourcing platforms. General linear analyses were performed to compare normative means between countries and continents adjusted for relevant covariates. Normative reference values were stratified by age, body mass index (BMI), and gender. The BODY-Q was completed by 4051 (2052 North American and 1999 European) participants. The mean age was 36 years (±14.7 SD) and ranged from 17 to 76 years, the mean BMI was 26.4 (±6.7 SD) kg/m2 , and the sample consisted of 1996 (49.3%) females and 2023 (49.9%) males. Younger age and higher BMI were negatively associated with all BODY-Q scales (p < .001). This study provides normative values for the BODY-Q scales to aid in the interpretation of BODY-Q scores in research and clinical practise. These values enable us to understand the impact of weight loss and BC on patients' lives.
Keywords: bariatric surgery; body contouring; general population norms; normative scores; patient-reported outcome measure; patient-reported outcomes; quality of life; weight loss surgery.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical Obesity published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of World Obesity Federation.
Conflict of interest statement
Anne F. Klassen and Andrea L. Pusic are co‐developers of the BODY‐Q and receive a share of any licence revenues based on their institutions inventor sharing policy. Anne F. Klassen is an owner of EVENTUM Research which provides consulting services to the pharmaceutical industry. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Obesity and overweight. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

