Animal Models to Investigate the Impact of Flavors on Nicotine Addiction and Dependence
- PMID: 35611777
- PMCID: PMC9886843
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X20666220524120231
Animal Models to Investigate the Impact of Flavors on Nicotine Addiction and Dependence
Abstract
Background: Tobacco use in humans is a long-standing public health concern. Flavors are common additives in tobacco and alternative tobacco products, added to mask nicotine's harsh orosensory effects and increase the appeal of these products. Animal models are integral for investigating nicotine use and addiction and are helpful for understanding the effects of flavor additives on the use of nicotine delivery products.
Objective: This review focuses on preclinical models to evaluate the contribution of flavor additives to nicotine addiction.
Materials and methods: An electronic literature search was conducted by authors up to May 2022. Original articles were selected.
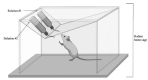
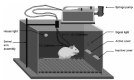
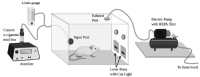
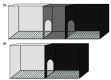
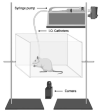
Results: The behavioral models of rodents described here capture multiple dimensions of human flavored nicotine use behaviors, including advantages and disadvantages.
Conclusion: The consensus of the literature search was that human research on nicotine use behavior has not caught up with fast-changing product innovations, marketing practices, and federal regulations. Animal models are therefore needed to investigate mechanisms underlying nicotine use and addiction. This review provides a comprehensive overvie.
Keywords: Nicotine; addiction; animal model; e-cigarettes; flavor; self-administration.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. 2021. (Accessed May 14, 2022). Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tobacco (Accessed May 14, 2022).
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2011: Warning about the Dangers of Tobacco; WHO Press. 2011
-
- World Health Organization, WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic 2008: The MPOWER Package ; WHO Press. 2008
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Smoking & Tobacco Use Health Effects; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, Georgia. 2020. Available from: https://www.cdc. gov/tobacco/basic_ information/health_effects/index.htm (Accessed May 14, 2022).
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Current Cigarette Smoking Among U.S. Adults Aged 18 Years and Older; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, Georgia. 2022. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/campaign/tips/resources/data/cigarette-smoki... (Accessed May 14, 2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

