A deep learning approach to detect blood vessels in basal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35611797
- PMCID: PMC9907638
- DOI: 10.1111/srt.13150
A deep learning approach to detect blood vessels in basal cell carcinoma
Abstract
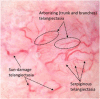
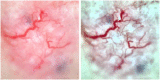
Purpose: Blood vessels called telangiectasia are visible in skin lesions with the aid of dermoscopy. Telangiectasia are a pivotal identifying feature of basal cell carcinoma. These vessels appear thready, serpiginous, and may also appear arborizing, that is, wide vessels branch into successively thinner vessels. Due to these intricacies, their detection is not an easy task, neither with manual annotation nor with computerized techniques. In this study, we automate the segmentation of telangiectasia in dermoscopic images with a deep learning U-Net approach.
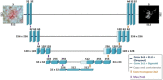
Methods: We apply a combination of image processing techniques and a deep learning-based U-Net approach to detect telangiectasia in digital basal cell carcinoma skin cancer images. We compare loss functions and optimize the performance by using a combination loss function to manage class imbalance of skin versus vessel pixels.
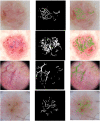
Results: We establish a baseline method for pixel-based telangiectasia detection in skin cancer lesion images. An analysis and comparison for human observer variability in annotation is also presented.
Conclusion: Our approach yields Jaccard score within the variation of human observers as it addresses a new aspect of the rapidly evolving field of deep learning: automatic identification of cancer-specific structures. Further application of DL techniques to detect dermoscopic structures and handle noisy labels is warranted.
Keywords: basal cell carcinoma; blood vessels; deep learning; dermoscopy; skin cancer; telangiectasia.
© 2022 The Authors. Skin Research and Technology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
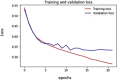

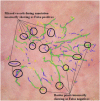
References
-
- Rogers HW, Weinstock MA, Feldman SR, Coldiron BM. Incidence estimate of nonmelanoma skin cancer (keratinocyte carcinomas) in the US population, 2012. JAMA Dermatol. 2012;151(10):1081–6. - PubMed
-
- Rigel DS, Torres AM, Ely HJ. Imiquimod 5% cream following curettage without electrodesiccation for basal cell carcinoma: preliminary report. J Drugs Dermatol.2008;7(1):15–6. - PubMed
-
- Marchetti MA, Codella NCF, Dusza SW, Gutman DA, Helba B, Kalloo A, et al. International Skin Imaging Collaboration. Results of the 2016 International Skin Imaging Collaboration International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging challenge: comparison of the accuracy of computer algorithms to dermatologists for the diagnosis of melanoma from dermoscopic images. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78(2):270–7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haenssle HA, Fink C, Toberer F, Winkler J, Stolz W, Deinlein T, et al. Man against machine reloaded: performance of a market‐approved convolutional neural network in classifying a broad spectrum of skin lesions in comparison with 96 dermatologists working under less artificial conditions. Ann Oncol. 2020; 31(1):137–43. 10.1016/j.annonc.2019.10.013. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

