Directed Evolution of PD-L1-Targeted Affibodies by mRNA Display
- PMID: 35611948
- PMCID: PMC10691555
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.2c00218
Directed Evolution of PD-L1-Targeted Affibodies by mRNA Display
Abstract
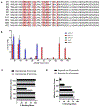
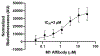
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies directed against PD-L1 (e.g., atezolizumab) disrupt PD-L1:PD-1 signaling and reactivate exhausted cytotoxic T-cells in the tumor compartment. Although anti-PD-L1 antibodies are successful as immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapeutics, there is still a pressing need to develop high-affinity, low-molecular-weight ligands for molecular imaging and diagnostic applications. Affibodies are small polypeptides (∼60 amino acids) that provide a stable molecular scaffold from which to evolve high-affinity ligands. Despite its proven utility in the development of imaging probes, this scaffold has never been optimized for use in mRNA display, a powerful in vitro selection platform incorporating high library diversity, unnatural amino acids, and chemical modification. In this manuscript, we describe the selection of a PD-L1-binding affibody by mRNA display. Following randomization of the 13 amino acids that define the binding interface of the well-described Her2 affibody, the resulting library was selected against recombinant human PD-L1 (hPD-L1). After four rounds, the enriched library was split and selected against either hPD-L1 or the mouse ortholog (mPD-L1). The dual target selection resulted in the identification of a human/mouse cross-reactive PD-L1 affibody (M1) with low nanomolar affinity for both targets. The M1 affibody bound with similar affinity to mPD-L1 and hPD-L1 expressed on the cell surface and inhibited signaling through the PD-L1:PD-1 axis at low micromolar concentrations in a cell-based functional assay. In vivo optical imaging with M1-Cy5 in an immune-competent mouse model of lymphoma revealed significant tumor uptake relative to a Cy5-conjugated Her2 affibody.
Figures

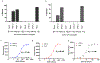
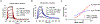

References
-
- De Silva P; Aiello M; Gu-Trantien C; Migliori E; Willard-Gallo K; Solinas C, Targeting CTLA-4 in cancer: Is it the ideal companion for PD-1 blockade immunotherapy combinations? Int J Cancer 2021, 149 (1), 31–41. - PubMed
-
- Thallinger C; Fureder T; Preusser M; Heller G; Mullauer L; Holler C; Prosch H; Frank N; Swierzewski R; Berger W, et al., Review of cancer treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors : Current concepts, expectations, limitations and pitfalls. Wien Klin Wochenschr 2018, 130 (3-4), 85–91. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Teng F; Meng X; Kong L; Yu J, Progress and challenges of predictive biomarkers of anti PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy: A systematic review. Cancer Lett 2018, 414, 166–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

