Merits and advances of microfluidics in the pharmaceutical field: design technologies and future prospects
- PMID: 35612293
- PMCID: PMC9154770
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2069878
Merits and advances of microfluidics in the pharmaceutical field: design technologies and future prospects
Abstract
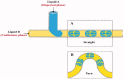
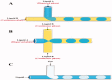
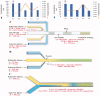
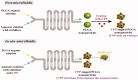
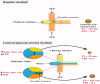
Microfluidics is used to manipulate fluid flow in micro-channels to fabricate drug delivery vesicles in a uniform tunable size. Thanks to their designs, microfluidic technology provides an alternative and versatile platform over traditional formulation methods of nanoparticles. Understanding the factors that affect the formulation of nanoparticles can guide the proper selection of microfluidic design and the operating parameters aiming at producing nanoparticles with reproducible properties. This review introduces the microfluidic systems' continuous flow (single-phase) and segmented flow (multiphase) and their different mixing parameters and mechanisms. Furthermore, microfluidic approaches for efficient production of nanoparticles as surface modification, anti-fouling, and post-microfluidic treatment are summarized. The review sheds light on the used microfluidic systems and operation parameters applied to prepare and fine-tune nanoparticles like lipid, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA)-based nanoparticles as well as cross-linked nanoparticles. The approaches for scale-up production using microfluidics for clinical or industrial use are also highlighted. Furthermore, the use of microfluidics in preparing novel micro/nanofluidic drug delivery systems is presented. In conclusion, the characteristic vital features of microfluidics offer the ability to develop precise and efficient drug delivery nanoparticles.
Keywords: Microfluidics; drug delivery; micromixers; nanoparticles; scale-up.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures
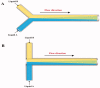
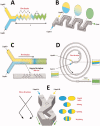
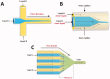
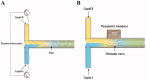
References
-
- Abate AR, Lee D, Do T, et al. (2008). Glass coating for PDMS microfluidic channels by sol-gel methods. Lab Chip 8:1549–8. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Salam FS, Elkheshen SA, Mahmoud AA, et al. (2020). In-situ forming chitosan implant-loaded with raloxifene hydrochloride and bioactive glass nanoparticles for treatment of bone injuries: Formulation and biological evaluation in animal model. Int J Pharm 580:119213. - PubMed
-
- Abou-Hassan A, Dufrêche JF, Sandre O, et al. (2009). Fluorescence confocal laser scanning microscopy for pH mapping in a coaxial flow microreactor: application in the synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 113:18097–105.
-
- Ahmed H, Stokke BT. (2021). Fabrication of monodisperse alginate microgel beads by microfluidic picoinjection: a chelate free approach. Lab Chip 21:2232–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
