Sedentary behavior and cancer-an umbrella review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35612669
- PMCID: PMC9209390
- DOI: 10.1007/s10654-022-00873-6
Sedentary behavior and cancer-an umbrella review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses have summarized the association between sedentary behavior (SB) and cancer. However, the level of evidence and the potential for risk of bias remains unclear. This umbrella review summarized the current data on SB in relation to cancer incidence and mortality, with a particular emphasis on assessing the risk of bias. We searched PubMed, Web of Science and Cochrane Database for systematic reviews and meta-analyses on the association between SB and cancer incidence and mortality. We also searched for recent observational studies not yet included in existing meta-analyses. We re-calculated summary risk estimates for cancer incidence and mortality using random effects models. We included 14 meta-analyses covering 17 different cancer sites from 77 original studies. We found that high SB levels increase the risk for developing ovarian, endometrial, colon, breast, prostate, and rectal cancers, with relative risks of 1.29 (95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.08-1.56), 1.29 (95% CI = 1.16-1.45), 1.25 (95% CI = 1.16-1.33), 1.08 (95% CI = 1.04-1.11), 1.08 (95% CI = 1.00-1.17), and 1.07 (95% CI = 1.01-1.12), respectively. Also, we found an increased risk of cancer mortality of 1.18 (95% CI = 1.09-1.26). Most associations between SB and specific cancer sites were supported by a "suggestive" level of evidence. High levels of SB are associated with increased risk of several types of cancer and increased cancer mortality risk.
Keywords: Cancer mortality; Cancer prevention; Meta-analysis; Sedentary behavior; Sitting time; Umbrella review.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Figures
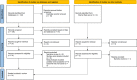
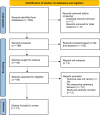


References
-
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–59. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

