Food-Specific IgG4 Antibody-Guided Exclusion Diet Improves Conditions of Patients with Chronic Pain
- PMID: 35612757
- PMCID: PMC9314524
- DOI: 10.1007/s40122-022-00391-z
Food-Specific IgG4 Antibody-Guided Exclusion Diet Improves Conditions of Patients with Chronic Pain
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic pain is related to gastrointestinal (GI) functions because food components affect inflammation and pain through their action on the GI immune and/or neural system and because many analgesics interact with the gut to alter its structure and function. Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) are food-specific antibodies resulting from exposure of the gut immune system to nutrients. High IgG4 levels have been found to be associated with inflammation.
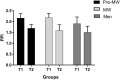
Methods: IgG4 were determined (both with the rapid test and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA) in men and women outpatients with chronic pain. All subjects were asked to exclude for 4 weeks all foods to which they had high blood levels of IgG4 antibodies. Pain and quality of life questionnaires were administered before (visit 1) and after (visit 2) the personalized exclusion diet period. Visual analogue scale (VAS), Italian Pain Questionnaire (QUID) and Margolis (MA) questionnaires were administered to determine pain intensity, pain features and pain extent, while Short Form Health Survey (SF-36) and Profile of Mood States (POMS) were used to test the quality of life and mood state. The nutritional status was evaluated in all subjects. Subject groups were women of reproductive age (pre-MW), women in menopause for at least 1 year (MW) and men.
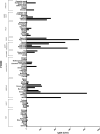
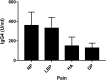
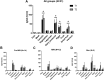
Results: Fifty-four subjects with chronic pain (n = 12 neuropathic, n = 14 diffuse pain, n = 11 headache, n = 17 low back pain) completed the two visits and the 1-month exclusion diet. At visit 1, 47 (87%) subjects showed medium/high levels of IgG4 to at least one food. The foods showing the highest IgG4 values were eggs, dairy products, cereals and dried fruit. At visit 2, IgG4 levels were decreased, increased or unchanged. In all groups, the 4-week exclusion diet resulted in a significant reduction in all pain measures and an improvement of quality of life parameters. In particular, at visit 2, the VAS score determined in the morning decreased by more than 50%.
Conclusions: A food elimination diet based on IgG4 antibody levels may be effective in reducing pain and improving quality of life in patients with chronic pain.
Keywords: Chronic pain; Gastrointestinal functions; IgG4.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Food-specific IgG4 antibody-guided exclusion diet improves symptoms and rectal compliance in irritable bowel syndrome.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jul;40(7):800-7. doi: 10.1080/00365520510015593. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16109655
-
Virtualized clinical studies to assess the natural history and impact of gut microbiome modulation in non-hospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 a randomized, open-label, prospective study with a parallel group study evaluating the physiologic effects of KB109 on gut microbiota structure and function: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled study.Trials. 2021 Apr 2;22(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05157-0. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33810796 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Crohn's Disease with an IgG4-Guided Exclusion Diet: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Dig Dis Sci. 2016 Apr;61(4):1148-57. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3987-z. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Dig Dis Sci. 2016. PMID: 26809868 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and nutritional assessment of GM plants and derived food and feed: the role of animal feeding trials.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Mar;46 Suppl 1:S2-70. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.02.008. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18328408 Review.
-
Final report on the safety assessment of capsicum annuum extract, capsicum annuum fruit extract, capsicum annuum resin, capsicum annuum fruit powder, capsicum frutescens fruit, capsicum frutescens fruit extract, capsicum frutescens resin, and capsaicin.Int J Toxicol. 2007;26 Suppl 1:3-106. doi: 10.1080/10915810601163939. Int J Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17365137 Review.
Cited by
-
The multifactorial approach and the food allergen-specific substitutive diet as a tool to manage and ameliorate adverse reactions to foodstuffs in adulthood: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial-the ALASKA study.Trials. 2024 Jul 20;25(1):494. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08307-2. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39033266 Free PMC article.
-
Pain-resolving immune mechanisms in neuropathic pain.Nat Rev Neurol. 2023 Apr;19(4):199-220. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00777-3. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36859719 Review.
-
The Impact of Food Specific IgG Antibodies on Migraine and Its Comorbidities.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Nov;12(11):e70056. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70056. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39552191 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

