The dynamic atmospheric and aeolian environment of Jezero crater, Mars
- PMID: 35613267
- PMCID: PMC9132482
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abn3783
The dynamic atmospheric and aeolian environment of Jezero crater, Mars
Erratum in
-
Erratum for the Research Article: "The dynamic atmospheric and aeolian environment of Jezero crater, Mars".Sci Adv. 2023 Feb 10;9(6):eadg5279. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg5279. Epub 2023 Feb 10. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 36763667 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
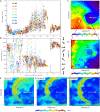
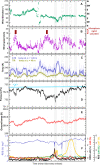
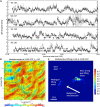
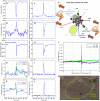
Despite the importance of sand and dust to Mars geomorphology, weather, and exploration, the processes that move sand and that raise dust to maintain Mars' ubiquitous dust haze and to produce dust storms have not been well quantified in situ, with missions lacking either the necessary sensors or a sufficiently active aeolian environment. Perseverance rover's novel environmental sensors and Jezero crater's dusty environment remedy this. In Perseverance's first 216 sols, four convective vortices raised dust locally, while, on average, four passed the rover daily, over 25% of which were significantly dusty ("dust devils"). More rarely, dust lifting by nonvortex wind gusts was produced by daytime convection cells advected over the crater by strong regional daytime upslope winds, which also control aeolian surface features. One such event covered 10 times more area than the largest dust devil, suggesting that dust devils and wind gusts could raise equal amounts of dust under nonstorm conditions.
Figures



Comment in
-
NASA's Perseverance rover begins key search for life on Mars.Nature. 2022 Jun;606(7914):441-442. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-01543-z. Nature. 2022. PMID: 35654970 No abstract available.
References
-
- Diniega S., Bramson A. M., Buratti B., Buhler P., Burr D. M., Chojnacki M., Conway S. J., Dundas C. M., Hansen C. J., McEwen A. S., Lapôtre M. G. A., Levy J., McKeown L., Piqueux S., Portyankina G., Swann C., Titus T. N., Widmer J. M., Modern Mars’ geomorphological activity, driven by wind, frost, and gravity. Geomorphology 380, 107627 (2021).
-
- Szwast M. A., Richardson M. I., Vasavada A. R., Surface dust redistribution on Mars as observed by the Mars Global Surveyor and Viking orbiters. J. Geophys. Res. 111, E11008 (2006).
-
- Viúdez-Moreiras D., Newman C. E., Torre M., Martínez G., Guzewich S., Lemmon M., Pla-García J., Smith M. D., Harri A. M., Genzer M., Vicente-Retortillo A., Lepinette A., Rodriguez-Manfredi J. A., Vasavada A. R., Gómez-Elvira J., Effects of the MY34/2018 global dust storm as measured by MSL REMS in Gale crater. J. Geophy. Res. 124, 1899–1912 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
-
- M. A. Kahre, J. R. Murphy, C. E. Newman, R. J. Wilson, B. A. Cantor, M. T. Lemmon, M. J. Wolff, The Mars dust cycle, in The Atmosphere and Climate of Mars, R. Haberle, R. T. Clancy, F. Forget, M. D. Smith, R. W. Zurek, Eds. (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2017), pp. 295–337.
-
- Greeley R., Bridges N. T., Kuzmin R. O., Laity J. E., Terrestrial analogs to wind-related features at the Viking and Pathfinder landing sites on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. 107, E1 (2002).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

