Quantitative and ultrasensitive in situ immunoassay technology for SARS-CoV-2 detection in saliva
- PMID: 35613342
- PMCID: PMC9132547
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abn3481
Quantitative and ultrasensitive in situ immunoassay technology for SARS-CoV-2 detection in saliva
Abstract
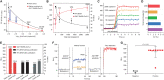
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has become an immense global health crisis. However, the lack of efficient and sensitive on-site testing methods limits early detection for timely isolation and intervention. Here, we present a quantitative and ultrasensitive in situ immunoassay technology for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) detection in saliva (QUIT SARS-CoV-2). Our nanoporous membrane resonator generates a rapid oscillating flow to purify and concentrate fully intact SARS-CoV-2 virus in saliva by 40-fold for in situ detection of viral antigens based on chemiluminescent immunoassay within 20 min. This method can not only achieve a detection sensitivity below 100 copies/ml of virus, comparable to the bench-top PCR equipment; it can also improve detection specificity via direct monitoring of viral loads. The integrated portable QUIT SARS-CoV-2 system, which enables rapid and accurate on-site viral screening with a high-throughput sample pooling strategy, can be performed in primary care settings and substantially improve the detection and prevention of COVID-19.
Figures

Update of
-
Quantitative and Ultrasensitive In-situ Immunoassay Technology for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Saliva.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2021 Jan 18:rs.3.rs-138025. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-138025/v1. Res Sq. 2021. Update in: Sci Adv. 2022 May 27;8(21):eabn3481. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn3481. PMID: 33469572 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Swelum A. A., Shafi M. E., Albaqami N. M., el-Saadony M. T., Elsify A., Abdo M., Taha A. E., Abdel-Moneim A. M. E., al-Gabri N. A., Almaiman A. A., Saleh al-wajeeh A., Tufarelli V., Staffa V. N., Abd el-Hack M. E., COVID-19 in human, animal, and environment: A review. Front. Vet. Sci. 7, 578 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

