Sites of vulnerability in HCV E1E2 identified by comprehensive functional screening
- PMID: 35613596
- PMCID: PMC9281441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110859
Sites of vulnerability in HCV E1E2 identified by comprehensive functional screening
Abstract
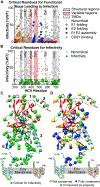
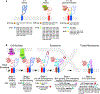
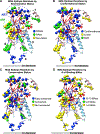
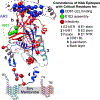
The E1 and E2 envelope proteins of hepatitis C virus (HCV) form a heterodimer that drives virus-host membrane fusion. Here, we analyze the role of each amino acid in E1E2 function, expressing 545 individual alanine mutants of E1E2 in human cells, incorporating them into infectious viral pseudoparticles, and testing them against 37 different monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to ascertain full-length translation, folding, heterodimer assembly, CD81 binding, viral pseudoparticle incorporation, and infectivity. We propose a model describing the role of each critical residue in E1E2 functionality and use it to examine how MAbs neutralize infection by exploiting functionally critical sites of vulnerability on E1E2. Our results suggest that E1E2 is a surprisingly fragile protein complex where even a single alanine mutation at 92% of positions disrupts its function. The amino-acid-level targets identified are highly conserved and functionally critical and can be exploited for improved therapies and vaccines.
Keywords: CP: Microbiology; E1E2 mutation library; E1E2 structure-function; flaviviridae; hepatitis C virus; hepatitis C virus infectivity.
Copyright © 2022 Integral Molecular, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.M.P.-K., E.D., K.K.-E., M.H., E.R., R.C., and B.J.D. are current or former employees of Integral Molecular. B.J.D. is a shareholder of Integral Molecular. J.E.C., Jr. has served as a consultant for Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, and Luna Biologics, is a member of the Scientific Advisory Boards of CompuVax and Meissa Vaccines, and is founder of IDBiologics. The J.E.C., Jr. laboratory at Vanderbilt University Medical Center has received sponsored research agreements from Takeda Vaccines, IDBiologics, and AstraZeneca.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Probing the antigenicity of hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein complex by high-throughput mutagenesis.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Dec 18;13(12):e1006735. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006735. eCollection 2017 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 29253863 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the role of putative CD81 binding regions of E2 in mediating HCV entry: putative CD81 binding region 1 is not involved in CD81 binding.Virol J. 2008 Mar 20;5:46. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-5-46. Virol J. 2008. PMID: 18355410 Free PMC article.
-
Functional expression and characterization of the envelope glycoprotein E1E2 heterodimer of hepatitis C virus.PLoS Pathog. 2019 May 22;15(5):e1007759. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007759. eCollection 2019 May. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31116791 Free PMC article.
-
Glycan Shielding and Modulation of Hepatitis C Virus Neutralizing Antibodies.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 27;9:910. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00910. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29755477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Modeling of Hepatitis C Virus Envelope Glycoprotein Structure and Recognition.Front Immunol. 2018 May 28;9:1117. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01117. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29892287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structures of the Hepaci-, Pegi-, and Pestiviruses envelope proteins suggest a novel membrane fusion mechanism.PLoS Biol. 2023 Jul 11;21(7):e3002174. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002174. eCollection 2023 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37432947 Free PMC article.
-
HCV E1 influences the fitness landscape of E2 and may enhance escape from E2-specific antibodies.Virus Evol. 2023 Nov 18;9(2):vead068. doi: 10.1093/ve/vead068. eCollection 2023. Virus Evol. 2023. PMID: 38107333 Free PMC article.
-
The hepatitis C virus envelope protein complex is a dimer of heterodimers.Nature. 2024 Sep;633(8030):704-709. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07783-5. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Nature. 2024. PMID: 39232163
-
Signatures of VH1-69-derived hepatitis C virus neutralizing antibody precursors defined by binding to envelope glycoproteins.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 7;14(1):4036. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39690-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37419906 Free PMC article.
-
The red alga Porphyridium as a host for molecular farming: Efficient production of immunologically active hepatitis C virus glycoprotein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jun 11;121(24):e2400145121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2400145121. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38833465 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alhammad Y, Gu J, Boo I, Harrison D, McCaffrey K, Vietheer PT, Edwards S, Quinn C, Coulibaly F, Poumbourios P, and Drummer HE (2015). Monoclonal antibodies directed toward the hepatitis C virus glycoprotein E2 detect antigenic differences modulated by the N-terminal hypervariable region 1 (HVR1), HVR2, and intergenotypic variable region. J. Virol 89, 12245–12261. 10.1128/jvi.02070-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

