Therapeutic potential of biogenic and optimized silver nanoparticles using Rubia cordifolia L. leaf extract
- PMID: 35614187
- PMCID: PMC9133087
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12878-y
Therapeutic potential of biogenic and optimized silver nanoparticles using Rubia cordifolia L. leaf extract
Abstract
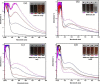
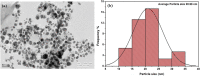
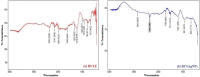
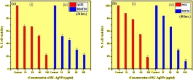
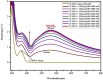
Rubia cordifolia L. is a widely used traditional medicine in the Indian sub-continent and Eastern Asia. In the present study, the aqueous leaf extract of the R. Cordifolia was used to fabricate silver nanoparticles (RC@AgNPs), following a green synthesis approach. Effect of temperature (60 °C), pH (8), as well the concentration of leaf extract (2 ml) and silver nitrate (2 mM) were optimized for the synthesis of stable RC@AgNPs. The phytofabrication of nanosilver was validated by UV-visible spectral analysis, which displayed a distinctive surface plasmon resonance peak at 432 nm. The effective functional molecules as capping and stabilizing agents, and responsible for the conversion of Ag+ to nanosilver (Ag0) were identified using the FTIR spectra. The spherical RC@AgNPs with an average size of ~ 20.98 nm, crystalline nature, and 61% elemental composition were revealed by TEM, SEM, XRD, and. EDX. Biogenic RC@AgNPs displayed a remarkable anticancer activity against B16F10 (melanoma) and A431 (carcinoma) cell lines with respective IC50 of 36.63 and 54.09 µg/mL, respectively. Besides, RC@AgNPs showed strong antifungal activity against aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus, DNA-binding properties, and DPPH and ABTS free radical inhibition. The presented research provides a potential therapeutic agent to be utilized in various biomedical applications.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Chandraker SK, Ghosh MK, Lal M, Shukla R. A review on plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles, their characterization and applications. Nano Express. 2021;2(2):022008. doi: 10.1088/2632-959X/ac0355. - DOI
-
- Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019;12(7):908–931. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

