SPECT Imaging of Acute Disc Herniation by Targeting Integrin α5β1 in Rat Models
- PMID: 35614922
- PMCID: PMC9124789
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.782967
SPECT Imaging of Acute Disc Herniation by Targeting Integrin α5β1 in Rat Models
Abstract
Objective: Traditional morphological imaging of intervertebral disc herniation (IVDH) is challenging in early disease diagnosis. Aiming at the early diagnosis of IVD by non-invasive molecular imaging targeting of integrin α5β1, we performed novel imaging in rats with acute IVDH for the first time.
Methods: Animal models were prepared by conducting an established needle puncture procedure through the normal intervertebral disc (IVD). The disc-injured rats underwent SPECT/CT imaging of the 99mTc-3PisoDGR2 peptide at 1 day to 2 months postinjury. The expression change of integrin α5β1 was determined by anti-integrin α5 and anti-integrin α5β1 immunohistochemistry (IHC). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed for comparison during disease progression. The morphological changes of the disc were determined by safranin-O staining.
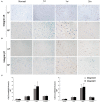
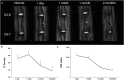
Results: Rats with acute IVDH showed gradually increased disc uptake of 99mTc-3PisoDGR2 from 1 to 7 days posttreatment, which was a significantly higher level than that of the normal disks in degenerative diseases. IHC results showed the expression of integrin α5β1 on the surface of annulus fibrosus (AF) cells and nucleus pulposus (NP) cells, which agreed with the uptake data. MRI showed a progressively decreased T2 density and MRI index throughout the investigation. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and safranin-O staining revealed a disorganized structure of the IVD as well as loss of proteoglycans after puncture.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrated a good correlation between integrin α5β1 expression and acute disc herniation. The SPECT/CT imaging of 99mTc-3PisoDGR2 targeting integrin α5β1 may diagnose IVDH in an acute phase for early disease management.
Keywords: 99mTc-3PisoDGR2; acute; disc herniation; integrin α5β1; molecular imaging.
Copyright © 2022 Guan, Yuan, Tian, Cheng, Gao, Yao, Wang, Wu, Chen and Jian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Total disc replacement using a tissue-engineered intervertebral disc in vivo: new animal model and initial results.Evid Based Spine Care J. 2010 Aug;1(2):62-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1100918. Evid Based Spine Care J. 2010. PMID: 23637671 Free PMC article.
-
Functional impact of integrin α5β1 on the homeostasis of intervertebral discs: a study of mechanotransduction pathways using a novel dynamic loading organ culture system.Spine J. 2015 Mar 1;15(3):417-26. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.12.143. Epub 2014 Dec 27. Spine J. 2015. PMID: 25546513 Free PMC article.
-
Improved in Vivo Targeting Capability and Pharmacokinetics of 99mTc-Labeled isoDGR by Dimerization and Albumin-Binding for Glioma Imaging.Bioconjug Chem. 2019 Jul 17;30(7):2038-2048. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00323. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Bioconjug Chem. 2019. PMID: 31063685
-
Diagnostic Imaging in Intervertebral Disc Disease.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Oct 22;7:588338. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.588338. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33195623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Immune Privilege of the Intervertebral Disc: Implications for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Treatment.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Feb 24;17(5):685-692. doi: 10.7150/ijms.42238. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32210719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

