The Impact of Endovascular Rescue Therapy on the Clinical and Radiological Outcome After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Safe and Effective Treatment Option for Hemodynamically Relevant Vasospasm?
- PMID: 35614929
- PMCID: PMC9124775
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.838456
The Impact of Endovascular Rescue Therapy on the Clinical and Radiological Outcome After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Safe and Effective Treatment Option for Hemodynamically Relevant Vasospasm?
Abstract
Objective: Cerebral vasospasm (CVS) represents one of the multiple contributors to delayed cerebral ischemia (DCI) in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH). Especially the management of CVS, refractory to medical treatment, is a challenging task during the acute phase after aSAH. Endovascular rescue therapies (ERT), such as medical and mechanical dilation, are possible treatment options on an individual basis. However, data about the influence on the patients' functional outcomes are limited. This study aims to assess the impact of ERT on the long-term functional outcome in aSAH-patients with refractory CVS.
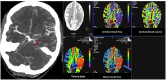
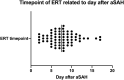
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of aSAH patients treated between 2012 and 2018. CVS was considered refractory, if it persisted despite oral/intravenous nimodipine application and induced hypertension. The decision to perform ETR was made on an individual basis, according to the detection of "tissue at risk" on computed tomography perfusion (CTP) scans and CVS on computed tomography angiography (CTA) or digital subtraction angiography (DSA). The functional outcome was assessed according to the modified Rankin scale (mRS) 3 months after the ictus, whereas an mRS ≤ 2 was considered as a good outcome.
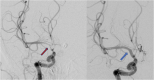
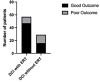
Results: A total of 268 patients were included. Out of these, 205 patients (76.5%) were treated without ERT (group 1) and 63 patients (23.5%) with ERT (group 2). In 20 patients (31.8%) balloon dilatation was performed, in 23 patients (36.5%) intra-arterial nimodipine injection alone, and in 20 patients (31.8%) both procedures were combined. Considering only the patient group with DCI, the patients who were treated with ERT had a significantly better outcome compared to the patients without ERT (Mann-Whitney test, p = 0.02).
Conclusion: Endovascular rescue therapies resulted in a significantly better functional outcome in patients with DCI compared to the patient group treated without ETR. CTP and CTA-based identification of "tissue at risk" might be a reliable tool for patient selection for performing ERT.
Keywords: cerebral vasospasm; endovascular therapy; endovascular treatment; outcome; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Copyright © 2022 Mielke, Döring, Behme, Psychogios, Rohde and Malinova.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Milrinone for refractory cerebral vasospasm with delayed cerebral ischemia.J Neurosurg. 2020 Mar 27;134(3):971-982. doi: 10.3171/2020.1.JNS193107. Print 2021 Mar 1. J Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32217799
-
Molsidomine for the prevention of vasospasm-related delayed ischemic neurological deficits and delayed brain infarction and the improvement of clinical outcome after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a single-center clinical observational study.J Neurosurg. 2016 Jan;124(1):51-8. doi: 10.3171/2014.12.JNS13846. Epub 2015 Jul 10. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26162034
-
Effectiveness of Continuous Intra-Arterial Nimodipine Infusion for the Treatment of Refractory Vasospasm after Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2025 Apr 16. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2025.0004. Online ahead of print. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2025. PMID: 40235034
-
Electroencephalography for detection of vasospasm and delayed cerebral ischemia in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a retrospective analysis and systematic review.Neurosurg Focus. 2022 Mar;52(3):E3. doi: 10.3171/2021.12.FOCUS21656. Neurosurg Focus. 2022. PMID: 35231893
-
CT perfusion imaging in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. State of the art.Front Radiol. 2024 Oct 7;4:1445676. doi: 10.3389/fradi.2024.1445676. eCollection 2024. Front Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39434941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum concentration-guided intravenous magnesium sulfate administration for neuroprotection in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a retrospective evaluation of a 12-year single-center experience.Neurosurg Rev. 2023 Sep 26;46(1):256. doi: 10.1007/s10143-023-02159-1. Neurosurg Rev. 2023. PMID: 37751032 Free PMC article.
-
Value of sildenafil treatment for the prevention of vasospasm‑related delayed ischemic neurological deficits and delayed brain infarction following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.Med Int (Lond). 2023 Mar 20;3(2):19. doi: 10.3892/mi.2023.79. eCollection 2023 Mar-Apr. Med Int (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37032716 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous Intra-arterial Infusion of Verapamil for Severe Vasospasm Treatment After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 Apr 19;17(4):e82561. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82561. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40390753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mijiti M, Mijiti P, Axier A, Amuti M, Guohua Z, Xiaojiang C, et al. . Incidence and predictors of angiographic vasospasm, symptomatic vasospasm and cerebral infarction in Chinese patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. PLoS ONE. (2016) 11:e0168657. 10.1371/journal.pone.0168657 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Macdonald RL, Kassell NF, Mayer S, Ruefenacht D, Schmiedek P, Weidauer S, et al. . Clazosentan to overcome neurological ischemia and infarction occurring after subarachnoid hemorrhage (CONSCIOUS-1): randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 dose-finding trial. Stroke. (2008) 39:3015–21. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.519942 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

