Statistical methods for Mendelian randomization in genome-wide association studies: A review
- PMID: 35615025
- PMCID: PMC9123217
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.05.015
Statistical methods for Mendelian randomization in genome-wide association studies: A review
Abstract
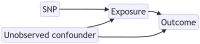
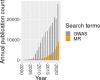
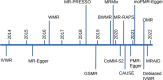
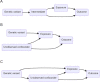
Genome-wide association studies have yielded thousands of associations for many common diseases and disease-related complex traits. The identified associations made it possible to identify the causal risk factors underlying diseases and investigate the causal relationships among complex traits through Mendelian randomization. Mendelian randomization is a form of instrumental variable analysis that uses SNP associations from genome-wide association studies as instruments to study and uncover causal relationships between complex traits. By leveraging SNP genotypes as instrumental variables, or proxies, for the exposure complex trait, investigators can tease out causal effects from observational data, provided that necessary assumptions are satisfied. We discuss below the development of Mendelian randomization methods in parallel with the growth of genome-wide association studies. We argue that the recent availability of GWAS summary statistics for diverse complex traits has motivated new Mendelian randomization methods with relaxed causality assumptions and that this area continues to offer opportunities for robust biological discoveries.
Keywords: Causal inference; Confounding; Genome-wide association study; Genomics; Horizontal pleiotropy; Mendelian randomization.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mendelian randomization for causal inference accounting for pleiotropy and sample structure using genome-wide summary statistics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 12;119(28):e2106858119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2106858119. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35787050 Free PMC article.
-
[Genetic Causation Analysis of Hyperandrogenemia Testing Indicators and Preeclampsia].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):566-573. doi: 10.12182/20240560106. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948277 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
An iterative approach to detect pleiotropy and perform Mendelian Randomization analysis using GWAS summary statistics.Bioinformatics. 2021 Jun 16;37(10):1390-1400. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa985. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33226062 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic Causal Inference Using Genome-Wide Association Study Data: Mendelian Randomization and Beyond.Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2022 Aug 10;5:1-17. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biodatasci-122120-024910. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2022. PMID: 35363507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mendelian randomization as a tool for causal inference in human nutrition and metabolism.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2021 Feb 1;32(1):1-8. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000721. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2021. PMID: 33278081 Review.
Cited by
-
Mediating role of circulating inflammatory proteins in the effect of immune cells on esophageal cancer risk: A Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 1;103(44):e40374. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040374. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39496002 Free PMC article.
-
Association between endometriosis and arthritis: results from NHANES 1999-2006, genetic correlation analysis, and Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 29;15:1424648. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1424648. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39136014 Free PMC article.
-
Causal links between serum micronutrients and epilepsy: a Mendelian randomization analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Jul 15;15:1419289. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1419289. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39076846 Free PMC article.
-
Causal associations of immune cell phenotypes with migraine: A mendelian randomization study.Mol Pain. 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17448069241274679. doi: 10.1177/17448069241274679. Mol Pain. 2024. PMID: 39083442 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic evidence for causal association between migraine and dementia: a mendelian randomization study.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Jul 5;17(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01956-x. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38970023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wright P.G. Macmillan Company; New York: 1928. Tariff on animal and vegetable oils.
-
- Wright S. Correlation and causation. J Agric Res. 1921;557–585
-
- Stock J.H., Trebbi F. Retrospectives: who invented instrumental variable regression? J Econ Perspect. 2003;17:177–194.
-
- Katan M. Apolipoprotein e isoforms, serum cholesterol, and cancer. Lancet. 1986;507–508 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
