Mental Time Travel and Time Reference Difficulties in Alzheimer's Disease: Are They Related? A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35615204
- PMCID: PMC9126194
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.858001
Mental Time Travel and Time Reference Difficulties in Alzheimer's Disease: Are They Related? A Systematic Review
Abstract
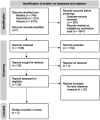
Mental time travel and language enable us to go back and forth in time and to organize and express our personal experiences through time reference. People with Alzheimer's disease have both mental time travel and time reference impairments, which can greatly impact their daily communication. Currently, little is known about the potential relationship between time conceptualization (i.e., mental time travel) and time reference difficulties in this disease. A systematic review of the literature was performed to determine if this link had already been investigated. Only three articles integrated both time conceptualization and time reference measures. However, the link between the two was not systematically analyzed and interpreted. This review highlights the lack of research addressing the question of the influence of time conceptualization impairments in Alzheimer's disease on other cognitive domains, and especially language.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; mental time travel; time conceptualization; time reference; verbal inflection.
Copyright © 2022 Schaffner, Sandoz, Grisot, Auclair-Ouellet and Fossard.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Albert M. S., DeKosky S. T., Dickson D., Dubois B., Feldman H. H., Fox N. C., et al. . (2011). The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7, 270–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Auclair-Ouellet N. (2015). Inflectional morphology in primary progressive aphasia and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. J. Neurol. 34, 41–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroling.2014.12.002 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources