Pulmonary Embolism Complicated With Cardiopulmonary Arrest Treated With Combination of Thrombolytics and Aspiration Thrombectomy
- PMID: 35615215
- PMCID: PMC9125515
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2022.03.028
Pulmonary Embolism Complicated With Cardiopulmonary Arrest Treated With Combination of Thrombolytics and Aspiration Thrombectomy
Abstract
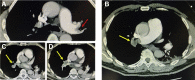
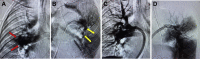
Systemic thrombolytic therapy is frequently used in the treatment of massive pulmonary embolism. We describe a case of pulseless electrical activity arrest, refractory obstructive shock in the setting of massive pulmonary embolism despite tissue plasminogen activator that was successfully treated with catheter-directed aspiration thrombectomy. (Level of Difficulty: Intermediate.).
Keywords: CCL, cardiac catheterization laboratory; CDTE, catheter directed thrombectomy; PE, pulmonary embolism; PEA, pulseless electrical activity; SpO2, oxygen saturation; VA-ECMO, veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; catheter directed thrombectomy; pulmonary embolism; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; thrombolytics.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Konstantinides S.V., Meyer G., Becattini C., et al. ESC Scientific Document Group, 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2020;41(4):543–603. - PubMed
-
- Kurkciyan I., Meron G., Sterz F., et al. Pulmonary embolism as cause of cardiac arrest. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:1529–1535. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

