Improved Sparrow Algorithm Based on Game Predatory Mechanism and Suicide Mechanism
- PMID: 35615547
- PMCID: PMC9126709
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4925416
Improved Sparrow Algorithm Based on Game Predatory Mechanism and Suicide Mechanism
Abstract
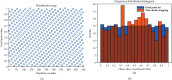
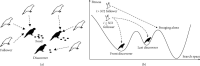
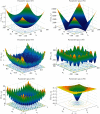
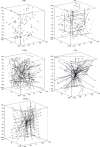
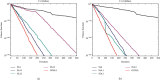
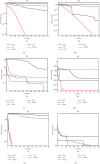
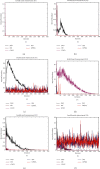
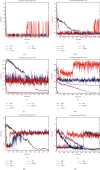
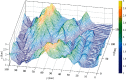
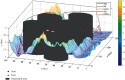
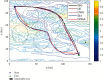
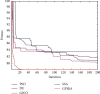
In order to overcome the defect that sparrow search algorithm converges very fast but is easy to fall into the trap of local optimization, based on the original mechanism of sparrow algorithm, this paper proposes game predatory mechanism and suicide mechanism, which makes sparrow algorithm more in line with its biological characteristics and enhances the ability of the algorithm to get rid of the attraction of local optimization while retaining the advantages of fast convergence speed. By initializing the population with the good point set strategy, the quality of the initial population is guaranteed and the diversity of the population is enhanced. In view of the current situation that the diversity index evaluation does not consider the invalid search caused by individuals beyond the boundary in the search process, an index to measure the invalid search beyond the boundary in the search process is proposed, and the measurement of diversity index is further improved to make it more accurate. The improved algorithm is tested on six basic functions and CEC2017 test function to verify its effectiveness. Finally, the improved algorithm is applied to the three-dimensional path planning of UAV with threat area. The results show that the improved algorithm has stronger optimization performance, has strong competitiveness compared with other algorithms, and can quickly plan the effective and stable path of UAV, which improves an effective method for the application in this field and other fields.
Copyright © 2022 Ping Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm Based on Iterative Local Search.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021 Dec 15;2021:6860503. doi: 10.1155/2021/6860503. eCollection 2021. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34956353 Free PMC article.
-
Intelligent Path Planning with an Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm for Workshop UAV Inspection.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;24(4):1104. doi: 10.3390/s24041104. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38400262 Free PMC article.
-
A Learning Sparrow Search Algorithm.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021 Aug 6;2021:3946958. doi: 10.1155/2021/3946958. eCollection 2021. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34413887 Free PMC article.
-
An Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm and Its Application in HIFU Sound Field.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Mar 3;2023:1228685. doi: 10.1155/2023/1228685. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36909963 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Versions and Applications of Sparrow Search Algorithm.Arch Comput Methods Eng. 2023;30(5):2831-2858. doi: 10.1007/s11831-023-09887-z. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Arch Comput Methods Eng. 2023. PMID: 36777699 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SecMDGM: Federated Learning Security Mechanism Based on Multi-Dimensional Auctions.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 2;22(23):9434. doi: 10.3390/s22239434. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36502140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu W. L., Gong Y. J., Chen W. N., Liu Z., Wang H., Zhang J. Coordinated charging scheduling of electric vehicles: A mixed-variable differential evolution approach [J] IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems . 2020;21(12):5094–5109. doi: 10.1109/tits.2019.2948596. - DOI
-
- Zhou S., Xing L., Zheng X., Du N., Wang L., Zhang Q. A self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm for scheduling a single batch-processing machine with arbitrary job sizes and release times [J] IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics . 2021;51(3):1430–1442. doi: 10.1109/tcyb.2019.2939219. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhao F., Zhao L., Wang L., Song H. An ensemble discrete differential evolution for the distributed blocking flowshop scheduling with minimizing makespan criterion. Expert Systems with Applications . 2020;160 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113678.113678 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

