Cell Based Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases in Children
- PMID: 35615628
- PMCID: PMC9124972
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2022.855260
Cell Based Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases in Children
Abstract
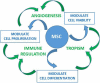
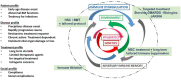
Mesenchymal stem cells have recently been recoined as medicinal signaling cells (MSC) for their ability to promote tissue homeostasis through immune modulation, angiogenesis and tropism. During the last 20 years, there has been a plethora of publications using MSC in adults and to lesser extent neonates on a variety of illnesses. In parts of the world, autologous and allogeneic MSCs have been purified and used to treat a range of autoimmune conditions, including graft versus host disease, Crohn's disease, multiple sclerosis, refractory systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis. Generally, these reports are not part of stringent clinical trials but are of note for good outcomes with minimal side effects. This review is to summarize the current state of the art in MSC therapy, with a brief discussion of cell preparation and safety, insights into mechanisms of action, and a review of published reports of MSC treatment of autoimmune diseases, toward the potential application of MSC in treatment of children with severe autoimmune diseases using multicenter clinical trials and treatment algorithms.
Keywords: autoimmune; children; mesenchymal; stem cells; transplant; treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Jones and McCurdy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mina R, von Scheven E, Ardoin SP, Eberhard BA, Punaro M, Ilowite N, et al. Consensus treatment plans for induction therapy of newly diagnosed proliferative lupus nephritis in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). (2012) 64:375–83. 10.1002/acr.21558 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huber AM, Robinson AB, Reed AM, Abramson L, Bout-Tabaku S, Carrasco R, et al. Consensus treatments for moderate juvenile dermatomyositis: beyond the first two months. Results of the second childhood arthritis and rheumatology research alliance consensus conference. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). (2012) 64:546–53. 10.1002/acr.20695 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

