A Shigella species variant is causally linked to intractable functional constipation
- PMID: 35617029
- PMCID: PMC9282927
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI150097
A Shigella species variant is causally linked to intractable functional constipation
Abstract
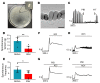
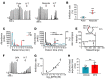
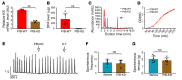
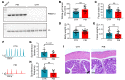
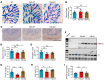
Intractable functional constipation (IFC) is the most severe form of constipation, but its etiology has long been unknown. We hypothesized that IFC is caused by refractory infection by a pathogenic bacterium. Here, we isolated from patients with IFC a Shigella species - peristaltic contraction-inhibiting bacterium (PIB) - that significantly inhibited peristaltic contraction of the colon by production of docosapentenoic acid (DPA). PIB colonized mice for at least 6 months. Oral administration of PIB was sufficient to induce constipation, which was reversed by PIB-specific phages. A mutated PIB with reduced DPA was incapable of inhibiting colonic function and inducing constipation, suggesting that DPA produced by PIB was the key mediator of the genesis of constipation. PIBs were detected in stools of 56% (38 of 68) of the IFC patients, but not in those of non-IFC or healthy individuals (0 of 180). DPA levels in stools were elevated in 44.12% (30 of 68) of the IFC patients but none of the healthy volunteers (0 of 97). Our results suggest that Shigella sp. PIB may be the critical causative pathogen for IFC, and detection of fecal PIB plus DPA may be a reliable method for IFC diagnosis and classification.
Keywords: Bacterial infections; Gastroenterology.
Figures

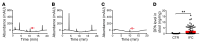

Comment in
-
Microbially derived polyunsaturated fatty acid as a modulator of gastrointestinal motility.J Clin Invest. 2022 Jul 15;132(14):e161572. doi: 10.1172/JCI161572. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35838050 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Signaling in Pathophysiology of Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction.Gastroenterology. 2022 Oct;163(4):1116-1117. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.07.010. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Gastroenterology. 2022. PMID: 35850193 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

