Outcomes of Retzius-sparing versus conventional robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: A KSER update series systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35617274
- PMCID: PMC9135208
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268182
Outcomes of Retzius-sparing versus conventional robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: A KSER update series systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy(RARP) is widely used to surgically treat of localized prostate cancer. Among RARP, retzius-sparing techniques(RS-RARP) are implemented through douglas pouch, not the existing conventional approach(C-RARP). We conducted an updated systematic review and meta-analysis including recent published papers.
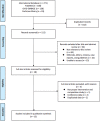
Materials & methods: Systematic review was performed following the PRISMA guideline. PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library were searched up to August 2021. We conducted meta-analysis as follows; Participants, patients with biopsy-proven PCa; Interventions, Patients underwent C-RARP or RS-RALP; Outcomes, comparison of continence recovery rate, positive surgical margins(PSM), complication, operation time and estimated blood loss(EBL) included for analysis.
Results: Thirteen studies with a total of 2917 patients were included for meta-analysis. Among them, three were randomized controlled trials (RCT) studies and the rest were non-RCT studies. Incontinence was analyzed with zero pad and safety pad, respectively. There showed a statistically significant advantage for RS-RARP in terms of continence recovery at 1 month(0 pad; OR 0.28, (0.16-0.47), safety-pad; OR 0.12 (0.07-0.22), p<0.001), as well as at 3 months(0 pad; OR 0.31 (0.18-0.53), safety-pad; OR 0.23 (0.14-0.40) p<0.001), 6 months(0 pad; OR 0.29 (0.17-0.51), safety-pad; OR 0.13 (0.06-0.27), p<0.001). And after 12 months, RS-RARP showed better results only in the safety-pad(0 pad; OR 0.64 (0.35-1.18), p = 0.15, safety-pad; OR 0.12 (0.04-0.36), p<0.001). In PSM, there was no statistical difference between two group at overall stage, but RS-RARP was observed to be higher than C-RARP in pT3 subgroup analysis(OR 0.74 (0.55-0.99), p = 0.047) (Fig 1). Whereas, there was no significant difference between the two groups in complication, operation time, and EBL.
Conclusions: Our analysis showed that RS-RARP is superior about early continence recovery than C-RARP. However, RS-RARP showed relatively high PSM in locally advanced PCa of pT3 or above. Therefore, although RS-RARP has few advantages about functional outcomes, we think that caution should be exercised when approaching patients with high-risk local diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Surgical and functional outcomes of Retzius-sparing robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy versus conventional robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy in patients with biopsy-confirmed prostate cancer. Are outcomes worth it? Systematic review and meta-analysis.Prostate. 2023 Nov;83(15):1395-1414. doi: 10.1002/pros.24604. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Prostate. 2023. PMID: 37555617
-
Retzius-sparing Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy Leads to Durable Improvement in Urinary Function and Quality of Life Versus Standard Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy Without Compromise on Oncologic Efficacy: Single-surgeon Series and Step-by-step Guide.Eur Urol. 2021 Jun;79(6):839-857. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.05.010. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Eur Urol. 2021. PMID: 32536488
-
Comparison of postoperative urinary continence and incontinence types between conventional and Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy.Neurourol Urodyn. 2023 Aug;42(6):1411-1420. doi: 10.1002/nau.25193. Epub 2023 Apr 25. Neurourol Urodyn. 2023. PMID: 37096807
-
Retzius sparing robotic assisted radical prostatectomy vs. conventional robotic assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Urol. 2020 May;38(5):1123-1134. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02798-4. Epub 2019 May 14. World J Urol. 2020. PMID: 31089802
-
Retzius-sparing versus standard robotic-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy for the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 18;8(8):CD013641. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013641.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32813279 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Retzius-Sparing Robotic-Assisted Prostatectomy: Technical Challenges for Surgeons and Key Prospective Refinements.Res Rep Urol. 2023 Dec 12;15:541-552. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S372803. eCollection 2023. Res Rep Urol. 2023. PMID: 38106985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of transperitoneal anterior, retzius-sparing, extraperitoneal, transvesical and perineal approaches on urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025 Jun;28(2):328-341. doi: 10.1038/s41391-025-00943-2. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2025. PMID: 39929994
-
Retzius-sparing vs. standard robot-assisted radical prostatectomy for clinically localised prostate cancer: a comparative study.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023 Sep;26(3):568-574. doi: 10.1038/s41391-022-00625-3. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2023. PMID: 36443438
-
Retzius-sparing radical prosatectomy: First 200 Australian cases.BJUI Compass. 2025 Feb 4;6(2):e489. doi: 10.1002/bco2.489. eCollection 2025 Feb. BJUI Compass. 2025. PMID: 39917586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forsmark A, Gehrman J, Angenete E, Bjartell A, Bjorholt I, Carlsson S, et al.. Health Economic Analysis of Open and Robot-assisted Laparoscopic Surgery for Prostate Cancer Within the Prospective Multicentre LAPPRO Trial. European Urology. 2018;74(6):816–24. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.07.038 WOS:000450121100030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yaxley JW, Coughlin GD, Chambers SK, Occhipinti S, Samaratunga H, Zajdlewicz L, et al.. Robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy versus open radical retropubic prostatectomy: early outcomes from a randomised controlled phase 3 study. Lancet. 2016;388(10049):1057–66. Epub 2016/07/31. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30592-X . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Freire MP, Weinberg AC, Lei Y, Soukup JR, Lipsitz SR, Prasad SM, et al.. Anatomic bladder neck preservation during robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: description of technique and outcomes. Eur Urol. 2009;56(6):972–80. Epub 2009/09/29. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.09.017 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

