Transcriptome sequencing of 3,3',4,4',5-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB126)-treated human preadipocytes demonstrates progressive changes in pathways associated with inflammation and diabetes
- PMID: 35618242
- PMCID: PMC9423686
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2022.105396
Transcriptome sequencing of 3,3',4,4',5-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB126)-treated human preadipocytes demonstrates progressive changes in pathways associated with inflammation and diabetes
Abstract
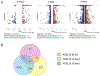
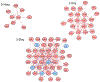
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are persistent organic pollutants that accumulate in adipose tissue and have been associated with cardiometabolic disease. We have previously demonstrated that exposure of human preadipocytes to the dioxin-like PCB126 disrupts adipogenesis via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). To further understand how PCB126 disrupts adipose tissue cells, we performed RNAseq analysis of PCB126-treated human preadipocytes over a 3-day time course. The most significant predicted upstream regulator affected by PCB126 exposure at the early time point of 9 h was the AhR. Progressive changes occurred in the number and magnitude of transcript levels of genes associated with inflammation, most closely fitting the pathways of cytokine-cytokine-receptor signaling and the AGE-RAGE diabetic complications pathway. Transcript levels of genes involved in the IL-17A, IL-1β, MAP kinase, and NF-κB signaling pathways were increasingly dysregulated by PCB126 over time. Our results illustrate the progressive time-dependent nature of transcriptional changes caused by toxicants such as PCB126, point to important pathways affected by PCB126 exposure, and provide a rich dataset for further studies to address how PCB126 and other AhR agonists disrupt preadipocyte function. These findings have implications for understanding how dioxin-like PCBs and other dioxin-like compounds are involved in the development of obesity and diabetes.
Keywords: Adipose; AhR; Inflammation; PCB126; Polychlorinated biphenyls; RNAseq.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


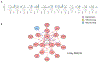
Similar articles
-
A delayed proinflammatory response of human preadipocytes to PCB126 is dependent on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Jun;25(17):16481-16492. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9676-z. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 28699004 Free PMC article.
-
Dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyl 126 (PCB126) disrupts gut microbiota-host metabolic dysfunction in mice via aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 May 1;236:113448. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113448. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022. PMID: 35367886
-
PCB126 blocks the thermogenic beiging response of adipocytes.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Mar;27(9):8897-8904. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06663-0. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31721030 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental dental toxicity of dioxin and related compounds--a review.Int Dent J. 2006 Dec;56(6):323-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1875-595x.2006.tb00336.x. Int Dent J. 2006. PMID: 17243464 Review.
-
Yusho and its latest findings-A review in studies conducted by the Yusho Group.Environ Int. 2015 Sep;82:41-8. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 23. Environ Int. 2015. PMID: 26010306 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation and cardiometabolic diseases induced by persistent organic pollutants and nutritional interventions: Effects of multi-organ interactions.Environ Pollut. 2023 Dec 15;339:122756. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.122756. Epub 2023 Oct 14. Environ Pollut. 2023. PMID: 37844865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polychlorinated biphenyls induce immunometabolic switch of antiinflammatory macrophages toward an inflammatory phenotype.PNAS Nexus. 2025 Mar 27;4(4):pgaf100. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf100. eCollection 2025 Apr. PNAS Nexus. 2025. PMID: 40191133 Free PMC article.
-
Dataset of transcriptomic changes that occur in human preadipocytes over a 3-day course of exposure to 3,3',4,4',5-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB126).Data Brief. 2022 Sep 1;45:108571. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108571. eCollection 2022 Dec. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 36131953 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity Impacts on Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells Acutely Exposed to Aroclor and Non-Aroclor Mixtures of Polychlorinated Biphenyl.Environ Sci Technol. 2023 Jan 31;57(4):1731-1742. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.2c07281. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Environ Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 36651682 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxylation markedly alters how the polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) congener, PCB52, affects gene expression in human preadipocytes.Toxicol In Vitro. 2023 Jun;89:105568. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2023.105568. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Toxicol In Vitro. 2023. PMID: 36804509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker NA, Karounos M, English V, Fang J, Wei Y, Stromberg A, Sunkara M, Morris AJ, Swanson HI, Cassis LA. 2013. Coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls impair glucose homeostasis in lean c57bl/6 mice and mitigate beneficial effects of weight loss on glucose homeostasis in obese mice. Environ Health Perspect. 121(1):105–110. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beyer A, Biziuk M. 2009. Environmental fate and global distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 201:137–158. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

