Repetitive Early 68Ga-FAPI PET Acquisition Comparing 68Ga-FAPI-02, 68Ga-FAPI-46, and 68Ga-FAPI-74: Methodologic and Diagnostic Implications for Malignant, Inflammatory/Reactive, and Degenerative Lesions
- PMID: 35618480
- PMCID: PMC9730916
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.122.264069
Repetitive Early 68Ga-FAPI PET Acquisition Comparing 68Ga-FAPI-02, 68Ga-FAPI-46, and 68Ga-FAPI-74: Methodologic and Diagnostic Implications for Malignant, Inflammatory/Reactive, and Degenerative Lesions
Abstract
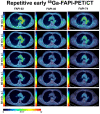
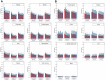
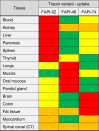
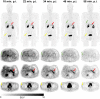
68Ga-labeled fibroblast activation protein (FAP) inhibitor (68Ga-FAPI) PET targets 68Ga-FAPI-positive activated fibroblasts and is a promising imaging technique for various types of cancer and nonmalignant pathologies. However, discrimination between malignant and nonmalignant 68Ga-FAPI-positive lesions based on static PET with a single acquisition time point can be challenging. Additionally, the optimal imaging time point for 68Ga-FAPI PET has not been identified yet, and different 68Ga-FAPI tracer variants are currently used. In this retrospective analysis, we evaluate the diagnostic value of repetitive early 68Ga-FAPI PET with 68Ga-FAPI-02, 68Ga-FAPI-46, and 68Ga-FAPI-74 for malignant, inflammatory/reactive, and degenerative lesions and describe the implications for future 68Ga-FAPI imaging protocols. Methods: Whole-body PET scans of 24 cancer patients were acquired at 10, 22, 34, 46, and 58 min after the administration of 150-250 MBq of 68Ga-FAPI tracer molecules (8 patients each for 68Ga-FAPI-02, 68Ga-FAPI-46, and 68Ga-FAPI-74). Detection rates and SUVs (SUVmax and SUVmean) for healthy tissues, cancer manifestations, and nonmalignant lesions were measured, and target-to-background ratios (TBR) versus blood and fat were calculated for all acquisition time points. Results: For most healthy tissues except fat and spinal canal, biodistribution analysis showed decreasing uptake over time. We analyzed 134 malignant, inflammatory/reactive, and degenerative lesions. Detection rates were minimally reduced for the first 2 acquisition time points and remained at a constant high level from 34 to 58 min after injection. The uptake of all 3 variants was higher in malignant and inflammatory/reactive lesions than in degenerative lesions. 68Ga-FAPI-46 showed the highest uptake and TBRs in all pathologies. For all variants, TBRs versus blood constantly increased over time for all pathologies, and TBRs versus fat were constant or decreased slightly. Conclusion: 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT is a promising imaging modality for malignancies and benign lesions. Repetitive early PET acquisition added diagnostic value for the discrimination of malignant from nonmalignant 68Ga-FAPI-positive lesions. High detection rates and TBRs over time confirmed that PET acquisition earlier than 60 min after injection delivers high-contrast images. Additionally, considering clinical feasibility, acquisition at 30-40 min after injection might be a reasonable compromise. Different 68Ga-FAPI variants show significant differences in time-dependent biodistributional behavior and should be selected carefully depending on the clinical setting.
Keywords: FAPI; PET; biodistribution; cancer; fibroblast activation protein.
© 2022 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Subclass Analysis of Malignant, Inflammatory and Degenerative Pathologies Based on Multiple Timepoint FAPI-PET Acquisitions Using FAPI-02, FAPI-46 and FAPI-74.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 28;14(21):5301. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215301. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358720 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of early and late 68Ga-FAPI-46-PET in 33 patients with possible recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 19;13(1):17848. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43049-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37857656 Free PMC article.
-
[18F]FAPI-42 PET imaging in cancer patients: optimal acquisition time, biodistribution, and comparison with [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Jul;49(8):2833-2843. doi: 10.1007/s00259-021-05646-z. Epub 2021 Dec 11. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34893920
-
How to Perform FAPI PET? An Expedited Systematic Review Providing a Recommendation for FAPI PET Imaging With Different FAPI Tracers.Semin Nucl Med. 2024 May;54(3):345-355. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2023.11.003. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Semin Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 38052711
-
Performance and Prospects of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI PET/CT Scans in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 13;14(22):5566. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225566. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428657 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of FAP imaging in lung cancer and beyond: a new chapter.Eur Radiol. 2024 Mar;34(3):1946-1947. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10398-5. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37943314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comparative analysis of two timepoints on [18F]FAPI-42 PET/CT in various cancers.Eur J Hybrid Imaging. 2023 Dec 11;7(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s41824-023-00186-1. Eur J Hybrid Imaging. 2023. PMID: 38072888 Free PMC article.
-
Value of [18F]AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT for differential diagnosis of malignant and various inflammatory lung lesions: comparison with [18F]FDG PET/CT.Eur Radiol. 2024 Mar;34(3):1948-1959. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10208-y. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37670186
-
FAP-Specific Signalling Is an Independent Diagnostic Approach in ACC and Not a Surrogate Marker of MRI Sequences.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;14(17):4253. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174253. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077788 Free PMC article.
-
Theranostics in targeting fibroblast activation protein bearing cells: Progress and challenges.Life Sci. 2023 Sep 15;329:121970. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121970. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37481033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kalluri R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:582–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
