Transcription factor-driven regulation of ILC1 and ILC3
- PMID: 35618586
- PMCID: PMC10166716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2022.04.009
Transcription factor-driven regulation of ILC1 and ILC3
Abstract
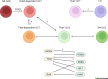
Mammalian innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) have functional relevance under both homeostatic and disease settings, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), particularly in the context of maintaining the integrity of mucosal surfaces. Early reports highlighted group 1 and 3 ILC regulatory transcription factors (TFs), T-box expressed in T cells (T-bet; Tbx21) and RAR-related orphan nuclear receptor γt (RORγt; Rorc), as key regulators of ILC biology. Since then, other canonical TFs have been shown to have a role in the development and function of ILC subsets. In this review, we focus on recent insights into the balance between mature ILC1 and ILC3 based on these TFs and how they interact with other key cell-intrinsic molecular pathways. We outline how this TF interplay might be explored to identify novel candidate therapeutic avenues for human diseases.
Keywords: innate lymphoid cells; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

