Depletion of skeletal muscle satellite cells attenuates pathology in muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 35618700
- PMCID: PMC9135721
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30619-7
Depletion of skeletal muscle satellite cells attenuates pathology in muscular dystrophy
Abstract
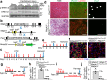
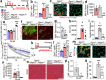
Skeletal muscle can repair and regenerate due to resident stem cells known as satellite cells. The muscular dystrophies are progressive muscle wasting diseases underscored by chronic muscle damage that is continually repaired by satellite cell-driven regeneration. Here we generate a genetic strategy to mediate satellite cell ablation in dystrophic mouse models to investigate how satellite cells impact disease trajectory. Unexpectedly, we observe that depletion of satellite cells reduces dystrophic disease features, with improved histopathology, enhanced sarcolemmal stability and augmented muscle performance. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that satellite cells initiate expression of the myogenic transcription factor MyoD, which then induces re-expression of fetal genes in the myofibers that destabilize the sarcolemma. Indeed, MyoD re-expression in wildtype adult skeletal muscle reduces membrane stability and promotes histopathology, while MyoD inhibition in a mouse model of muscular dystrophy improved membrane stability. Taken together these observations suggest that satellite cell activation and the fetal gene program is maladaptive in chronic dystrophic skeletal muscle.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
These authors, R.J.K. and C.W.W., declare the following competing interest; Owners of Myologica, a contract research organization specialized in assessing physiologic muscle function in the mouse. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

