Chromosome organization affects genome evolution in Sulfolobus archaea
- PMID: 35618771
- PMCID: PMC9597579
- DOI: 10.1038/s41564-022-01127-7
Chromosome organization affects genome evolution in Sulfolobus archaea
Abstract
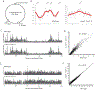
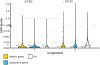
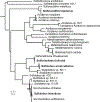
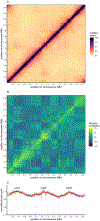
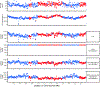
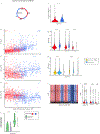
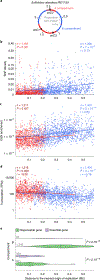
In all organisms, the DNA sequence and the structural organization of chromosomes affect gene expression. The extremely thermophilic crenarchaeon Sulfolobus has one circular chromosome with three origins of replication. We previously revealed that this chromosome has defined A and B compartments that have high and low gene expression, respectively. As well as higher levels of gene expression, the A compartment contains the origins of replication. To evaluate the impact of three-dimensional organization on genome evolution, we characterized the effect of replication origins and compartmentalization on primary sequence evolution in eleven Sulfolobus species. Using single-nucleotide polymorphism analyses, we found that distance from an origin of replication was associated with increased mutation rates in the B but not in the A compartment. The enhanced polymorphisms distal to replication origins suggest that replication termination may have a causal role in their generation. Further mutational analyses revealed that the sequences in the A compartment are less likely to be mutated, and that there is stronger purifying selection than in the B compartment. Finally, we applied the Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) to show that the B compartment is less accessible than the A compartment. Taken together, our data suggest that compartmentalization of chromosomal DNA can influence chromosome evolution in Sulfolobus. We propose that the A compartment serves as a haven for stable maintenance of gene sequences, while sequences in the B compartment can be diversified.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




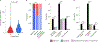


Similar articles
-
Evolutionary rates and gene dispensability associate with replication timing in the archaeon Sulfolobus islandicus.Genome Biol Evol. 2010;2:859-69. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evq068. Epub 2010 Oct 26. Genome Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20978102 Free PMC article.
-
Three replication origins in Sulfolobus species: synchronous initiation of chromosome replication and asynchronous termination.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 May 4;101(18):7046-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400656101. Epub 2004 Apr 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15107501 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple origins of replication in archaea.Trends Microbiol. 2004 Sep;12(9):399-401. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.07.001. Trends Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15337158 Review.
-
Physical and Functional Compartmentalization of Archaeal Chromosomes.Cell. 2019 Sep 19;179(1):165-179.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.08.036. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31539494 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging views of genome organization in Archaea.J Cell Sci. 2020 May 18;133(10):jcs243782. doi: 10.1242/jcs.243782. J Cell Sci. 2020. PMID: 32423947 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How Do Thermophiles Organize Their Genomes?Microbes Environ. 2024;39(5):ME23087. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME23087. Microbes Environ. 2024. PMID: 38839371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanopore sequencing reveals that DNA replication compartmentalisation dictates genome stability and instability in Trypanosoma brucei.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 16;16(1):751. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56087-3. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39820334 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin landscape of the euryarchaeon Haloferax volcanii.Genome Biol. 2023 Nov 6;24(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-03095-5. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 37932847 Free PMC article.
-
Correction of non-random mutational biases along a linear bacterial chromosome by the mismatch repair endonuclease NucS.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 May 22;52(9):5033-5047. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae132. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38444149 Free PMC article.
-
Hi-C/3C-seq Data Analysis for Prokaryotic Genomes with HiC-Pro.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2856:157-176. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4136-1_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39283451
References
-
- Mitelman F, Johansson B & Mertens F The impact of translocations and gene fusions on cancer causation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 233–245 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

