Astrocyte-targeted gene delivery of interleukin 2 specifically increases brain-resident regulatory T cell numbers and protects against pathological neuroinflammation
- PMID: 35618831
- PMCID: PMC9174055
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-022-01208-z
Astrocyte-targeted gene delivery of interleukin 2 specifically increases brain-resident regulatory T cell numbers and protects against pathological neuroinflammation
Abstract
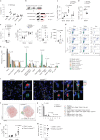
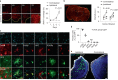
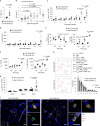
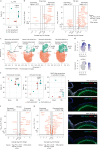
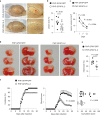
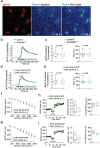
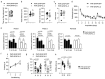
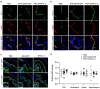
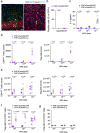
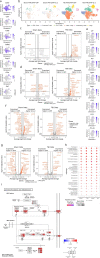
The ability of immune-modulating biologics to prevent and reverse pathology has transformed recent clinical practice. Full utility in the neuroinflammation space, however, requires identification of both effective targets for local immune modulation and a delivery system capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. The recent identification and characterization of a small population of regulatory T (Treg) cells resident in the brain presents one such potential therapeutic target. Here, we identified brain interleukin 2 (IL-2) levels as a limiting factor for brain-resident Treg cells. We developed a gene-delivery approach for astrocytes, with a small-molecule on-switch to allow temporal control, and enhanced production in reactive astrocytes to spatially direct delivery to inflammatory sites. Mice with brain-specific IL-2 delivery were protected in traumatic brain injury, stroke and multiple sclerosis models, without impacting the peripheral immune system. These results validate brain-specific IL-2 gene delivery as effective protection against neuroinflammation, and provide a versatile platform for delivery of diverse biologics to neuroinflammatory patients.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The VIB and Babraham Institute are owners of patent PCT/GB2020/052148 based on work included in the manuscript, with L.Y., E.P., J.D., M.G.H. and A.L. potential financial beneficiaries of commercialization. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








Comment in
-
CNS Treg cells have alternative functions but run on conventional fuel.Nat Immunol. 2022 Jun;23(6):818-819. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01201-6. Nat Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35618830 No abstract available.
-
Gene therapy protects against neuroinflammation.Nat Rev Neurol. 2022 Jul;18(7):381. doi: 10.1038/s41582-022-00683-0. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35676371 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barres BA. The mystery and magic of glia: a perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron. 2008;60:430–440. - PubMed
-
- Dokalis N, Prinz M. Resolution of neuroinflammation: mechanisms and potential therapeutic option. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41:699–709. - PubMed
-
- Gilhus NE, Deuschl G. Neuroinflammation—a common thread in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019;15:429–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

