Muscle spindles of the multifidus muscle undergo structural change after intervertebral disc degeneration
- PMID: 35618974
- PMCID: PMC7613463
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-022-07235-6
Muscle spindles of the multifidus muscle undergo structural change after intervertebral disc degeneration
Abstract
Purpose: Proprioceptive deficits are common in low back pain. The multifidus muscle undergoes substantial structural change after back injury, but whether muscle spindles are affected is unclear. This study investigated whether muscle spindles of the multifidus muscle are changed by intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration in a large animal model.
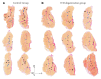
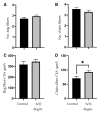
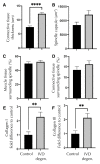
Methods: IVD degeneration was induced by partial thickness annulus fibrosus lesion to the L3-4 IVD in nine sheep. Multifidus muscle tissue at L4 was harvested at six months after lesion, and from six age-/sex-matched naïve control animals. Muscle spindles were identified in Van Gieson's-stained sections by morphology. The number, location and cross-sectional area (CSA) of spindles, the number, type and CSA of intrafusal fibers, and thickness of the spindle capsule were measured. Immunofluorescence assays examined Collagen I and III expression.
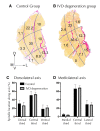
Results: Multifidus muscle spindles were located centrally in the muscle and generally near connective tissue. There were no differences in the number or location of muscle spindles after IVD degeneration and only changes in the CSA of nuclear chain fibers. The thickness of connective tissue surrounding the muscle spindle was increased as was the expression of Collagen I and III.
Conclusion: Changes to the connective tissue and collagen expression of the muscle spindle capsule are likely to impact their mechanical properties. Changes in capsule stiffness may impact the transmission of length change to muscle spindles and thus transduction of sensory information. This change in muscle spindle structure may explain some of the proprioceptive deficits identified with low back pain.
Keywords: Connective tissue; Intervertebral disc degeneration; Multifidus; Muscle spindle; Proprioception.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
ISSLS Prize in Basic Science 2025: Structural changes of muscle spindles in the multifidus muscle after intervertebral disk injury are resolved by targeted activation of the muscle.Eur Spine J. 2025 May;34(5):1600-1613. doi: 10.1007/s00586-025-08646-x. Epub 2025 Jan 15. Eur Spine J. 2025. PMID: 39810036
-
Targeted multifidus muscle activation reduces fibrosis of multifidus muscle following intervertebral disc injury.Eur Spine J. 2024 Jun;33(6):2166-2178. doi: 10.1007/s00586-024-08234-5. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 38607406
-
Macrophage polarization contributes to local inflammation and structural change in the multifidus muscle after intervertebral disc injury.Eur Spine J. 2018 Aug;27(8):1744-1756. doi: 10.1007/s00586-018-5652-7. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Eur Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29948327
-
Treatment of the degenerated intervertebral disc; closure, repair and regeneration of the annulus fibrosus.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015 Oct;9(10):1120-32. doi: 10.1002/term.1866. Epub 2014 Feb 25. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015. PMID: 24616324 Review.
-
Gut-disc axis: A cause of intervertebral disc degeneration and low back pain?Eur Spine J. 2022 Apr;31(4):917-925. doi: 10.1007/s00586-022-07152-8. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Eur Spine J. 2022. PMID: 35286474 Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of a 12-week combined motor control exercise and isolated lumbar extension intervention on lumbar multifidus muscle stiffness in individuals with chronic low back pain.Front Physiol. 2024 Aug 26;15:1336544. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1336544. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39258113 Free PMC article.
-
Biomechanical effects of altered multifidus muscle morphology on cervical spine tissues.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 20;13:1524844. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1524844. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40051837 Free PMC article.
-
Quantity and Distribution of Muscle Spindles in Animal and Human Muscles.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 3;25(13):7320. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137320. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
International Society for the Advancement of Spine Surgery Statement: Restorative Neurostimulation for Chronic Mechanical Low Back Pain Resulting From Neuromuscular Instability.Int J Spine Surg. 2023 Oct;17(5):728-750. doi: 10.14444/8525. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Int J Spine Surg. 2023. PMID: 37562978 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic Proteoglycans for Intervertebral Disc (IVD) Regeneration.Biomimetics (Basel). 2024 Nov 22;9(12):722. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics9120722. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39727726 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hodges PW, James G, Blomster L, Hall L, Schmid A, Shu C, Little C, Melrose J. Multifidus muscle changes after back injury are characterized by structural remodeling of muscle, adipose and connective tissue, but not muscle atrophy: Molecular and morphological evidence. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2015;40:1057–1071. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000972. - DOI - PubMed
-
- James G, Klyne DM, Millecamps M, Stone LS, Hodges PW. ISSLS Prize in Basic science 2019: Physical activity attenuates fibrotic alterations to the multifidus muscle associated with intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Spine J Off Publ Eur Spine Soc Eur Spinal Deform Soc Eur Sect Cerv Spine Res Soc. 2019 doi: 10.1007/s00586-019-05902-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

