Coronavirus disease 2019 transmission and symptoms in young children during the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Delta variant and Omicron variant outbreaks
- PMID: 35619217
- PMCID: PMC9150257
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605221102079
Coronavirus disease 2019 transmission and symptoms in young children during the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Delta variant and Omicron variant outbreaks
Abstract
Objective: Little is known about the transmission of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in young children. This study aimed to clarify the risk of COVID-19 transmission among this population.
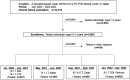
Methods: Between July 2020 and April 2022, 1660 0 to 3-year-old children underwent a nasopharyngeal swab for later reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction testing at a mass screening test center in Japan. Their disease transmission rate and clinical symptoms were evaluated according to the predominant variant strains of that season.
Results: The secondary transmission rate after close contact of the Delta B.1.617.2 (17.4%) and Omicron B.1.1.529 (39.2%) variants was significantly higher than that of the conventional strains (B.1.1.284 and B.1.1.214; 4.5%) during the pandemic. The increased transmissibility with the Delta and Omicron variants was independent of close contact or location. The prevalence rates of cough, fatigability, and fever were similar in young children infected by the Delta and Omicron variants.
Conclusions: COVID-19 transmission in children aged 0 to 3 years increased by 3 to 4 fold during the Delta outbreak and by 8 to 10 fold during the Omicron outbreak compared with the conventional strain outbreak. The symptoms in young children were not different between the Delta and Omicron variants.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Delta; Omicron; symptom; transmission; variant strain; young child.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Reis G, Dos Santos Moreira-Silva EA, Silva DCM, et al.. Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial. Lancet Glob Health 2022; 10: e42–e51. 20211028. DOI: 10.1016/s2214-109x(21)00448-4. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants, https://www.who.int/en/activities/tracking-SARS-CoV-2-variants/.
-
- Song P, Karako T. The strategy behind Japan's response to COVID-19 from 2020–2021 and future challenges posed by the uncertainty of the Omicron variant in 2022. Biosci Trends 2022; 15: 350–352. 20211228. DOI: 10.5582/bst.2021.01560. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

