Changes in the Small Noncoding RNAome During M1 and M2 Macrophage Polarization
- PMID: 35619693
- PMCID: PMC9127141
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.799733
Changes in the Small Noncoding RNAome During M1 and M2 Macrophage Polarization
Abstract
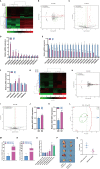
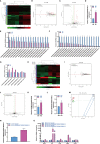
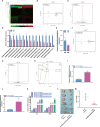
Macrophages belong to a special phagocytic subgroup of human leukocytes and are one of the important cells of the human immune system. Small noncoding RNAs are a group of small RNA molecules that can be transcribed without the ability to encode proteins but could play a specific function in cells. SncRNAs mainly include microRNAs (miRNAs) and piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and repeat RNAs. We used high-throughput sequencing analysis and qPCR to detect the expression changes of the small noncoding RNAome during macrophage polarization. Our results showed that 84 miRNAs and 47 miRNAs with were downregulated during M1 macrophage polarization and that 11 miRNAs were upregulated and 19 miRNAs were downregulated during M2 macrophage polarization. MiR-novel-3-nature and miR-27b-5p could promote expression of TNF-α which was marker gene of M1 macrophages. The piRNA analysis results showed that 69 piRNAs were upregulated and 61 piRNAs were downregulated during M1 macrophage polarization and that 3 piRNAs were upregulated and 10 piRNAs were downregulated during M2 macrophage polarization. DQ551351 and DQ551308 could promote the mRNA expression of TNF-α and DQ551351overexpression promoted the antitumor activity of M1 macrophages. SnoRNA results showed that 62 snoRNAs were upregulated and 59 snoRNAs were downregulated during M1 macrophage polarization, whereas 6 snoRNAs were upregulated and 10 snoRNAs were downregulated during M2 macrophage polarization. Overexpression of snoRNA ENSMUST00000158683.2 could inhibit expression of TNF-α. For snRNA, we found that 12 snRNAs were upregulated and 15 snRNAs were downregulated during M1 macrophage polarization and that 2 snRNAs were upregulated during M2 macrophage polarization. ENSMUSG00000096786 could promote expression of IL-1 and iNOS and ENSMUSG00000096786 overexpression promoted the antitumor activity of M1 macrophages. Analysis of repeat RNAs showed that 7 repeat RNAs were upregulated and 9 repeat RNAs were downregulated during M1 macrophage polarization and that 2 repeat RNAs were downregulated during M2 macrophage polarization. We first reported the expression changes of piRNA, snoRNA, snRNA and repeat RNA during macrophage polarization, and preliminarily confirmed that piRNA, snoRNA and snRNA can regulate the function of macrophages.
Keywords: macrophage polarization; miRNA; piRNA; repeat RNA; snRNA; snoRNA.
Copyright © 2022 Ma, Zhou, Wang, Dai, Yuan, Peng, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Changes in the small noncoding RNA transcriptome in osteosarcoma cells.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Nov 24;18(1):898. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04362-8. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 38001513 Free PMC article.
-
Ox-LDL induced profound changes of small non-coding RNA in rat endothelial cells.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 7;10:1060719. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1060719. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36824457 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Small Noncoding RNA Expression during Chondrocyte Senescence.Cartilage. 2022 Jul-Sep;13(3):19476035221118165. doi: 10.1177/19476035221118165. Cartilage. 2022. PMID: 35993268 Free PMC article.
-
Disorders and roles of tsRNA, snoRNA, snRNA and piRNA in cancer.J Med Genet. 2022 Jul;59(7):623-631. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2021-108327. Epub 2022 Feb 10. J Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 35145038 Review.
-
MiRNA-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and its Potential Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response.Shock. 2016 Aug;46(2):122-31. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000604. Shock. 2016. PMID: 26954942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatoma cell-derived exosomal SNORD52 mediates M2 macrophage polarization by activating the JAK2/STAT6 pathway.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jan 13;16(1):36. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01700-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39804511 Free PMC article.
-
FindAdapt: A python package for fast and accurate adapter detection in small RNA sequencing.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Jan 22;20(1):e1011786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011786. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38252662 Free PMC article.
-
High aspect ratio nanomaterial-induced macrophage polarization is mediated by changes in miRNA levels.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 27;14:1111123. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1111123. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36776851 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin enhances the efficacy of glucantime to modulate macrophage polarization toward the M1 phenotype in Leishmania tropica-infected macrophages.Parasit Vectors. 2025 Aug 25;18(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s13071-025-07004-6. Parasit Vectors. 2025. PMID: 40855340 Free PMC article.
-
Novel roles of PIWI proteins and PIWI-interacting RNAs in human health and diseases.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Nov 29;21(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01368-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38031146 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

