A Case Report of Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome in a Patient With Systemic Scleroderma
- PMID: 35619870
- PMCID: PMC9126427
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.24364
A Case Report of Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome in a Patient With Systemic Scleroderma
Abstract
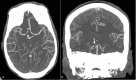
Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS) is represented by recurrent severe thunderclap headache, with or without neurological symptoms. RCVS can be primary or secondary to several factors. Here, we present a case of RCVS in a patient with systemic scleroderma. A 44-year-old female patient presented to the hospital due to Raynaud's phenomenon, fingertip pain ulceration, skin tightness, and skin depigmentation. She was diagnosed with systemic scleroderma. After four days of steroids, immunosuppressants (mycophenolate mofetil), and hydroxychloroquine, the patient developed severe thunderclap headaches and left lower extremity weakness. The computed tomography angiography (CTA) showed multifocal segmental vasoconstriction of the cerebral arteries. The patient's headache and body weakness resolved after starting an oral calcium channel blocker (nimodipine).
Keywords: calcium channel blocker; immunosuppressants; reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome; steroid; systemic scleroderma.
Copyright © 2022, Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome: recognition and treatment. Cappelen-Smith C, Calic Z, Cordato D. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017;19:21. - PubMed
-
- Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Calic Z, Cappelen-Smith C, Zagami AS. Intern Med J. 2015;45:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ashraf VV, Bhasi R, Ramakrishnan KG, Praveenkumar R, Girija AS. Neurol India. 2012;60:635–637. - PubMed
-
- A systemic lupus erythematosus patient with thunderclap headache: reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome. Chung SW, Lee KM, Heo SH, et al. Lupus. 2019;28:898–902. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
