Clinical Application Effects of Different Preoperative Blood Management Schemes in Older Patients with Delayed Intertrochanteric Fracture Surgery
- PMID: 35620020
- PMCID: PMC9129265
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S362020
Clinical Application Effects of Different Preoperative Blood Management Schemes in Older Patients with Delayed Intertrochanteric Fracture Surgery
Abstract
Introduction: Research on preoperative blood management in older patients with delayed surgery for intertrochanteric fracture is scarce, especially regarding hematopoiesis and hemostasis. We assessed the effectiveness of optimized blood management programs in older patients undergoing delayed surgery for intertrochanteric fractures.
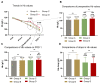
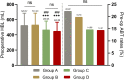
Methods: This retrospective study included 456 patients who underwent delayed surgery for intertrochanteric fractures. According to the optimized blood management plan, the patients were divided into four groups: group A was the control group; group B received 1 g of tranexamic acid (TXA) intravenously at admission; group C underwent sequential TXA treatment after admission until 1 day before surgery (1 g/day); and group D received iron supplements (200 mg/day) in addition to the treatment administered to group C, with or without recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEPO; 40,000 IU). The primary outcomes were preoperative hidden blood loss (HBL), preoperative allogeneic blood transfusion (ABT) rate, hemoglobin (Hb) change, and actual Hb drop.
Results: The Hb reduction, calculated HBL, and hospitalization duration in groups C and D were significantly lower than those in groups A and B. The preoperative ABT rates in groups C and D were significantly lower than those in groups A and B, with no significant difference between groups C and D.
Discussion: The results of this study suggested that iron supplementation (with or without rHuEPO) combined with the sequential IV TXA scheme did not show a better clinical effect than the sequential IV TXA scheme in the management of patients undergoing delayed surgery for intertrochanteric fractures. Therefore, further evaluation is needed before recommending iron supplements and rHuEPO in older patients.
Keywords: blood management; intertrochanteric fractures; iron supplements; surgical delay; tranexamic acid.
© 2022 Cui et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of post-traumatic antifibrinolysis in the perioperative blood management of elderly patients with intertrochanteric fractures treated with PFNA: A randomised controlled trial.Injury. 2024 Dec;55(12):111877. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2024.111877. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Injury. 2024. PMID: 39504735 Clinical Trial.
-
[Efficacy and safety of intravenous combined with topical administration of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss after intramedullary fixation of intertrochanteric femoral fractures].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 May 15;35(5):550-555. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202010040. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33998206 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effectiveness and safety of an optimized blood management program in total hip and knee arthroplasty: A large, single-center, retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jan;97(1):e9429. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009429. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29505518 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in the treatment of intertrochanteric fracture: an updated meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020 Aug;50(2):243-257. doi: 10.1007/s11239-019-02034-1. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2020. PMID: 31902124
-
Efficacy and safety of intravenous tranexamic acid administration in patients undergoing hip fracture surgery for hemostasis: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 May;96(21):e6940. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006940. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28538384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suboptimal Use of DOACs Post-Discharge for Geriatric Hip Fractures with Isolated Calf Deep Vein Thrombosis: Do Clinician Prescribing Preferences and Patient Compliance Alters Clinical Outcomes?Clin Interv Aging. 2023 Aug 28;18:1423-1436. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S421422. eCollection 2023. Clin Interv Aging. 2023. PMID: 37663122 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative Administration of Tranexamic Acid and Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Enhanced Blood Management in Intertrochanteric Fractures: A Randomized Controlled Study.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Jun 14;30:e944063. doi: 10.12659/MSM.944063. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 38875178 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Robot-assisted PFNA surgery improves clinical outcomes in the treatment of unstable femoral intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients compared with traditional PFNA surgery.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 30;15(1):3836. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88229-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39885317 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

