Chromatin Regulators Ahc1p and Eaf3p Positively Influence Nitrogen Metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 35620110
- PMCID: PMC9127870
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.883934
Chromatin Regulators Ahc1p and Eaf3p Positively Influence Nitrogen Metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
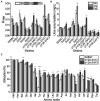
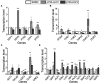
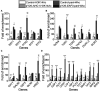
There is a complex regulatory network of nitrogen metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and many details of this regulatory network have not been revealed. This study explored the global regulation of nitrogen metabolism in S. cerevisiae from an epigenetic perspective. Comparative transcriptome analysis of S. cerevisiae S288C treated with 30 nitrogen sources identified nine chromatin regulators (CRs) that responded significantly to different nitrogen sources. Functional analysis showed that among the CRs identified, Ahc1p and Eaf3p promoted the utilization of non-preferred nitrogen sources through global regulation of nitrogen metabolism. Ahc1p regulated nitrogen metabolism through amino acid transport, nitrogen catabolism repression (NCR), and the Ssy1p-Ptr3p-Ssy5p signaling sensor system. Eaf3p regulated nitrogen metabolism via amino acid transport and NCR. The regulatory mechanisms of the effects of Ahc1p and Eaf3p on nitrogen metabolism depended on the function of their histone acetyltransferase complex ADA and NuA4. These epigenetic findings provided new insights for a deeper understanding of the nitrogen metabolism regulatory network in S. cerevisiae.
Keywords: Ahc1p; Eaf3p; amino acid utilization; histone acetylation; nitrogen preference.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Zeng, Ma, Ma and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chromatin regulator Eaf3p regulates nitrogen metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a trans-acting factor.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Dec 21;89(12):e0145723. doi: 10.1128/aem.01457-23. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38047643 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin regulator Ahc1p co-regulates nitrogen metabolism via interactions with multiple transcription factors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023 Jun 25;662:31-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.04.006. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37099808
-
Gene co-expression network analysis reveals the positive impact of endocytosis and mitochondria-related genes over nitrogen metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Gene. 2022 May 5;821:146267. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146267. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35150821
-
Regulation of Sensing, Transportation, and Catabolism of Nitrogen Sources in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018 Feb 7;82(1):e00040-17. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00040-17. Print 2018 Jun. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29436478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitrogen catabolite repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biotechnol. 1999 Aug;12(1):35-73. doi: 10.1385/MB:12:1:35. Mol Biotechnol. 1999. PMID: 10554772 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin regulator Eaf3p regulates nitrogen metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a trans-acting factor.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Dec 21;89(12):e0145723. doi: 10.1128/aem.01457-23. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38047643 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key genes through the constructed CRISPR-dcas9 to facilitate the efficient production of O-acetylhomoserine in Corynebacterium glutamicum.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 14;10:978686. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.978686. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36185436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cigic I. K., Vodosek T. V., Kosmerl T., Strlic M. (2008). Amino acid quantification in the presence of sugars using HPLC and pre-column derivatization with 3-MPA/OPA and FMOC-cl. Acta Chim. Slov. 2, 165–175. doi: 10.1021/nn700226y - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

