Metabolomic Mechanisms of Radix Fici Hirtae against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Damage in Mice
- PMID: 35620409
- PMCID: PMC9129960
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9157465
Metabolomic Mechanisms of Radix Fici Hirtae against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Damage in Mice
Abstract
Background: Radix Fici Hirtae (RFH), known as Cantonese ginseng, is an alternative folk medicine that is widely used to treat various diseases in southern China. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect and metabolic mechanisms of pretreatment with RFH on the serum metabolic profiles of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induced acute liver injury in mice.
Methods: Mice fed with the water extract of RFH at a dose of 1.5 g/kg and 0.75 g/kg for consecutive 7 days, and then serum samples were taken for the metabolomic analysis. Furthermore, the bioinformatics and pathways analysis were measured.
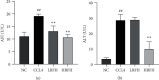
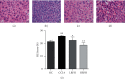
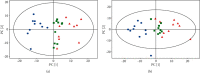
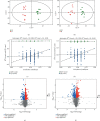
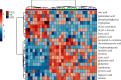
Results: The UHPLC-Orbitrap/MS based-metabolomic analysis identified 20 differential metabolic markers in serum of CCl4-induced liver injury mice compared to that of the normal controls, which were mainly related to the metabolism of amino acids and fatty acids. Furthermore, most of these biomarkers contributing to CCl4 induction were ameliorated by RFH, and the bioinformatics and pathways analysis revealed that therapeutic actions of RFH were mainly involved in the regulation of the oxidative stress responses and energy homeostasis.
Conclusion: These findings provide potential metabolic mechanism for future study and allow for hypothesis generation about the hepatoprotective effects of Radix Fici Hirtae.
Copyright © 2022 Fang-Yu Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

