Association of a Novel DOCK2 Mutation-Related Gene Signature With Immune in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35620462
- PMCID: PMC9127407
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.872224
Association of a Novel DOCK2 Mutation-Related Gene Signature With Immune in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
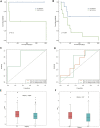
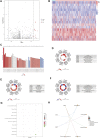
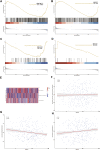
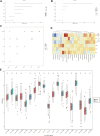
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a malignant tumor with high morbidity and mortality worldwide. Many studies have shown that dedicator of cytokinesis 2 (DOCK2) has a crucial role as a prognostic factor in various cancers. However, the potentiality of DOCK2 in the diagnosis of HCC has not been fully elucidated. In this work, we aimed to investigate the prognostic role of DOCK2 mutation in HCC. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) cohorts were utilized to identify the mutation frequency of DOCK2. Then, univariate Cox proportional hazard regression analysis, random forest (RF), and multivariate Cox regression analysis were performed to develop the risk score that was significantly related to DOCK2 mutation. Moreover, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA), Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA), and immune correlation analysis were conducted for an in-depth study of the biological process of DOCK2 mutation involved in HCC. The results revealed that the mutation frequency of DOCK2 was relatively higher than that in non-cancer control subjects, and patients with DOCK2 mutations had a low survival rate and a poor prognosis compared with the DOCK2-wild group. In addition, the secretin receptor (SCTR), tetratricopeptide repeat, ankyrin repeat and coiled-coil domain-containing 1 (TANC1), Alkb homolog 7 (ALKBH7), FRAS1-related extracellular matrix 2 (FREM2), and G protein subunit gamma 4 (GNG4) were found to be the most relevant prognostic genes of DOCK2 mutation, and the risk score based on the five genes played an excellent role in predicting the status of survival, tumor mutation burden (TMB), and microsatellite instability (MSI) in DOCK2 mutant patients. In addition, DOCK2 mutation and the risk score were closely related to immune responses. In conclusion, the present study identifies a novel prognostic signature in light of DOCK2 mutation-related genes that shows great prognostic value in HCC patients; and this gene mutation might promote tumor progression by influencing immune responses. These data may provide valuable insights for future investigations into personalized forecasting methods and also shed light on stratified precision oncology treatment.
Keywords: DOCK2; biomarker; hepatocellular carcinoma; immune; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Luo, Chen, Su, Zhu, Wei, Qiu, Long, Shi and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Prognostic Model of 15 Immune-Related Gene Pairs Associated With Tumor Mutation Burden for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Nov 13;7:581354. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.581354. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33282911 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of a Novel Six-Gene Expression Signature for Predicting Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prognosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 1;12:723271. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.723271. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925311 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis reveals a metabolic ten-gene signature in hepatocellular carcinoma.PeerJ. 2020 May 26;8:e9201. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9201. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32518728 Free PMC article.
-
Five metastasis-related mRNAs signature predicting the survival of patients with liver hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jun 11;21(1):693. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08431-1. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34116652 Free PMC article.
-
Insights from DOCK2 in cell function and pathophysiology.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Sep 29;9:997659. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.997659. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36250020 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disclosing transcriptomics network-based signatures of glioma heterogeneity using sparse methods.BioData Min. 2023 Sep 26;16(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13040-023-00341-1. BioData Min. 2023. PMID: 37752578 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a novel diagnostic model to monitor the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease to hepatocellular carcinoma in females.Discov Oncol. 2024 Dec 19;15(1):812. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01636-3. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39699604 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of multi-omics biomarkers and construction of the novel prognostic model for hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 15;12(1):12084. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16341-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35840618 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

