Development of a Cardio-Oncology Service in Lithuania: Prediction, Prevention, Monitoring and Treatment of Cancer Treatment-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 35621845
- PMCID: PMC9147714
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd9050134
Development of a Cardio-Oncology Service in Lithuania: Prediction, Prevention, Monitoring and Treatment of Cancer Treatment-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
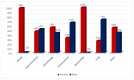
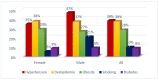
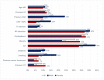
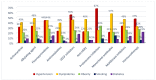
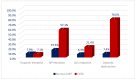
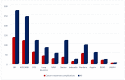
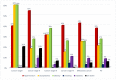
Background: Advances in cancer therapy have dramatically improved outcomes for cancer pa-tients. However, cancer treatment can cause several cardiovascular (CV) complications, increasing cardiac mortality and morbidity in cancer patients and survivors. As a result, a new cardiology subspecialty—cardio-oncology (CO)—has been developed. The goals of CO are to understand the mechanism of the cardiotoxicity (CTX) of cancer therapies and invent the best monitoring and treatment strategies to improve the survival of cancer patients. Methods: We performed a retro-spective observational study reporting on the 6-year experience of the first CO service in Vilnius, Lithuania. Cancer patients were consulted by a single part-time specialist at Vilnius University Hospital. All new patients underwent blood tests, including cardiac biomarkers and advanced transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) with stress protocol if indicated. During a follow-up, we evaluated the association of patient survival with such variables as age, gender, reasons for re-ferral, cancer location and stage, cardiovascular (CV) risk factors (RF), and rates and stage of CTX and treatment strategies. Results: 447 patients were consulted (70% females), and the median age was 64 years. Cardiovascular (CV) RF was common: 38.5% of patients had hypertension, almost 38% had dyslipidemia, 29% were obese, 10% were smokers, and 9% had diabetes. Nearly 26% of patients had a history of HF. Early biochemical cardiotoxicity was determined in 27%, early functional cardiotoxicity was seen in 17%, and early mixed cardiotoxicity—in 45% of referred patients treated with cardiotoxic cancer therapies. In addition, reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was found in 7% of patients. Beta-blockers (BB) were administered to 61.1% of patients, while angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers (ACEI/ARB) to 54.1% of patients. In addition, 18.3% of patients received loop diuretics and almost 12% mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), respectively. A total of 143 patients died during the 6-year follow-up period. The leading cause of death was primarily cancer (92.3%). Only in 5.6% of patients, cardiovascular complications were reported as the cause of death, and 2.1% of deaths were due to the COVID−19 infection. We found that age (HR 1.020 [95% CI: (1.005−1.036)] p = 0.009); LV diastolic dysfunction (HR 1.731 [95% CI: 1.115−2.689] p = 0.015; NYHA stage II (HR 2.016 [95% CI: 1.242−3.272] p = 0.005; NYHA stage III (HR 3.545 [95% CI: 1.948−6.450] p < 0.001; kidney dysfunction (HR 2.085 [95% CI: 1.377−3.159] p = 0.001; previous cancer (HR 2.004 [95% CI: 1.219−3.295] p = 0.006); tumor progression (HR 1.853 [95% CI: 1.217−2.823] p = 0.004) and lung cancer (HR 2.907 [95%CI: 1.826−4.627] p < 0.001) were statistically significantly associated with the increased risk of all-cause death. Conclusions: CO is a rapidly growing subspecialty of cardiology that aims to remove cardiac disease as a barrier to effective cancer treatment by preventing and reversing cardiac damage caused by cancer therapies. Establishing a CO service requires a cardiologist with an interest in oncology. Continuous education, medical training, and clinical research are crucial to success. Age, previous cancer, tumor progression, kidney dysfunction, left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, and NYHA stages were associated with increased mortality.
Keywords: cancer; cardio-oncology; cardio-oncology service; cardiotoxicity; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of heart failure pharmacotherapies in patients with heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024 Aug 22;31(11):1347-1360. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwae121. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38513366
-
Factors predisposing to ventricular tachyarrhythmia leading to appropriate ICD intervention in patients with coronary artery disease or non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy.Kardiol Pol. 2012;70(12):1264-75. Kardiol Pol. 2012. PMID: 23264245
-
Determinants of patient survival rate after implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator without resynchronisation capability.Kardiol Pol. 2012;70(11):1099-110. Kardiol Pol. 2012. PMID: 23180517
-
Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: a review of clinical risk factors, pharmacologic prevention, and cardiotoxicity of other HER2-directed therapies.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jul;188(1):21-36. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06280-x. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34115243 Review.
-
Cardio-oncology, the myth of Sisyphus, and cardiovascular disease in breast cancer survivors.Heart Fail Rev. 2019 Nov;24(6):977-987. doi: 10.1007/s10741-019-09805-1. Heart Fail Rev. 2019. PMID: 31134427 Review.
Cited by
-
Ivabradine for the Prevention of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Female Patients with Primarily Breast Cancer: A Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label Clinical Trial.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Dec 9;59(12):2140. doi: 10.3390/medicina59122140. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 38138243 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cardiovascular Toxicity Related to Cancer Treatment.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Jun 14;10(6):259. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10060259. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37367424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- [(accessed on 24 September 2021)]. Available online: https://stat.hi.lt/default.aspx?report_id=256.
-
- Ervik M., Lam F., Laversanne M., Ferlay J., Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer over Time; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France. [(accessed on 24 September 2021)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/overtime.
-
- Zamorano J.L., Lancellotti P., Rodriguez Muñoz D., Aboyans V., Asteggiano R., Galderisi M., Habib G., Lenihan D.J., Lip G.Y.H., Lyon A.R., et al. 2016 ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: The Task Force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur. Heart J. 2016;37:2768–2801. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw211. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nagueh S.F., Smiseth O.A., Appleton C.P., Byrd B.F., 3rd, Dokainish H., Edvardsen T., Flachskampf F.A., Gillebert T.C., Klein A.L., Lancellotti P., et al. Recommendations for the Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function by Echocardiography: An Update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2016;29:277–314. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2016.01.011. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

