Significance of α-Myosin Heavy Chain (MYH6) Variants in Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome and Related Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 35621855
- PMCID: PMC9147009
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd9050144
Significance of α-Myosin Heavy Chain (MYH6) Variants in Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome and Related Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
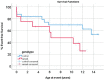
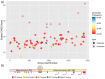
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a severe congenital heart disease (CHD) with complex genetic inheritance. HLHS segregates with other left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) malformations in families, and can present as either an isolated phenotype or as a feature of a larger genetic disorder. The multifactorial etiology of HLHS makes it difficult to interpret the clinical significance of genetic variants. Specific genes have been implicated in HLHS, including rare, predicted damaging MYH6 variants that are present in >10% of HLHS patients, and which have been shown to be associated with decreased transplant-free survival in our previous studies. MYH6 (α-myosin heavy chain, α-MHC) variants have been reported in HLHS and numerous other CHDs, including LVOT malformations, and may provide a genetic link to these disorders. In this paper, we outline the MYH6 variants that have been identified, discuss how bioinformatic and functional studies can inform clinical decision making, and highlight the importance of genetic testing in HLHS.
Keywords: cardiac myosin heavy chain; congenital heart disease; hypoplastic left heart syndrome; rare variant analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- McBride K.L., Pignatelli R., Lewin M., Ho T., Fernbach S., Menesses A., Lam W., Leal S.M., Kaplan N., Schliekelman P., et al. Inheritance analysis of congenital left ventricular outflow tract obstruction malformations: Segregation, multiplex relative risk, and heritability. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2005;134A:180–186. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30602. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

