Preclinical Development of Seriniquinones as Selective Dermcidin Modulators for the Treatment of Melanoma
- PMID: 35621952
- PMCID: PMC9143531
- DOI: 10.3390/md20050301
Preclinical Development of Seriniquinones as Selective Dermcidin Modulators for the Treatment of Melanoma
Abstract
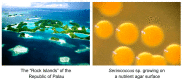
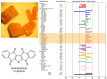
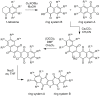
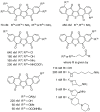
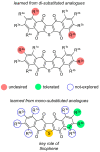
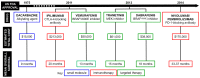
The bioactive natural product seriniquinone was discovered as a potential melanoma drug, which was produced by the as-yet-undescribed marine bacterium of the rare genus Serinicoccus. As part of a long-term research program aimed at the discovery of new agents for the treatment of cancer, seriniquinone revealed remarkable in vitro activity against a diversity of cancer cell lines in the US National Cancer Institute 60-cell line screening. Target deconvolution studies defined the seriniquinones as a new class of melanoma-selective agents that act in part by targeting dermcidin (DCD). The targeted DCD peptide has been recently examined and defined as a "pro-survival peptide" in cancer cells. While DCD was first isolated from human skin and thought to be only an antimicrobial peptide, currently DCD has been also identified as a peptide associated with the survival of cancer cells, through what is believed to be a disulfide-based conjugation with proteins that would normally induce apoptosis. However, the significantly enhanced potency of seriniquinone was of particular interest against the melanoma cell lines assessed in the NCI 60-cell line panel. This observed selectivity provided a driving force that resulted in a multidimensional program for the discovery of a usable drug with a new anticancer target and, therefore, a novel mode of action. Here, we provided an overview of the discovery and development efforts to date.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; dermcidin; marine natural products; melanoma; seriniquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Trzoss L., Fukuda T., Costa-Lotufo L.V., Jimenez P., La Clair J.J., Fenical W. Seriniquinone, a selective anticancer agent, induces cell death by autophagocytosis, targeting the cancer-protective protein dermcidin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:14687–14692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1410932111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ishida K., Tanaka T., Nagai K., Furuichi Y., Terahara T., Anda M., Tsukamasa Y., Fukuda T. New dihydronaphthothiophene derivatives by the biological transformation of seriniquinone using marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces albogriseolus OM27-12. J. Antibiot. 2022;65:9–15. doi: 10.1038/s41429-021-00484-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

