Botulinum Toxin Injection for the Treatment of Upper Esophageal Sphincter Dysfunction
- PMID: 35622568
- PMCID: PMC9147508
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14050321
Botulinum Toxin Injection for the Treatment of Upper Esophageal Sphincter Dysfunction
Abstract
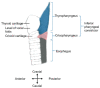
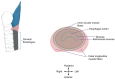
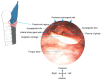
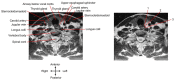
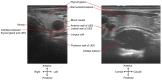
Dysphagia associated with upper esophageal sphincter (UES) dysfunction remarkably affects the quality of life of patients. UES injection of botulinum toxin is an effective treatment for dysphagia. In comparison with skeletal muscles of the limb and trunk, the UES is a special therapeutic target of botulinum toxin injection, owing to its several anatomical, physiological, and pathophysiological features. This review focuses on (1) the anatomy and function of the UES and the pathophysiology of UES dysfunction in dysphagia and why the entire UES rather than the cricopharyngeal muscle before/during botulinum toxin injection should be examined and targeted; (2) the therapeutic mechanisms of botulinum toxin for UES dysfunction, including the choice of injection sites, dose, and volume; (3) the strengths and weaknesses of guiding techniques, including electromyography, ultrasound, computed tomography, and balloon catheter dilation for botulinum toxin injection of the UES.
Keywords: botulinum toxin; cricopharyngeal muscle; dysphagia; electromyography; injection; ultrasound; upper esophageal sphincter.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment for upper esophageal sphincter dysfunction in a patient with poststroke dysphagia: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Mar;98(13):e14988. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014988. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30921211 Free PMC article.
-
Design and implementation of botulinum toxin on cricopharyngeal dysfunction guided by a combination of catheter balloon, ultrasound, and electromyography (BECURE) in patients with stroke: study protocol for a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Mar 31;22(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05195-8. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33789722 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum toxin A injection of UES in schizencephaly with dysphagia: Case report.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Nov;79(11):1935-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 26351064
-
Dysphagia in neurological diseases: a literature review.Neurol Sci. 2020 Nov;41(11):3067-3073. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-04495-2. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32506360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of upper esophageal sphincter disorders: indications and complications of myotomy.Am J Med. 2000 Mar 6;108 Suppl 4a:43S-46S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(99)00334-4. Am J Med. 2000. PMID: 10718451 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect and mechanism of motor imagery based on action observation treatment on dysphagia in Wallenberg Syndrome: a randomized controlled trial.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2024 Dec;60(6):938-948. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.24.08471-5. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2024. PMID: 39374050 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Drugs in focus: Botulinum toxin in the therapy of gastrointestinal disorders in children.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2024 Dec;79(6):1096-1105. doi: 10.1002/jpn3.12376. Epub 2024 Sep 24. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39315663 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Treatment of Post COVID-19 Neurogenic Dysphagia with Botulinum Toxin.Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2023 Nov 27;10(12):004105. doi: 10.12890/2023_004105. eCollection 2023. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 38077706 Free PMC article.
-
Management of dysphagia and gastroparesis in Parkinson's disease in real-world clinical practice - Balancing pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Aug 11;14:979826. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.979826. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36034128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound-Guided Botulinum Neurotoxin Injection for Alleviating Cricopharyngeus Muscle Spasticity: A Cadaveric Feasibility Study with Nerve Ending Analysis.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Jul 12;16(7):317. doi: 10.3390/toxins16070317. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39057957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Espinosa-Val M.C., Martín-Martínez A., Graupera M., Arias O., Elvira A., Cabré M., Palomera E., Bolívar-Prados M., Clavé P., Ortega O. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Complications of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Older Patients with Dementia. Nutrients. 2020;12:863. doi: 10.3390/nu12030863. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

