Neutralizing Anti-Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor Autoantibodies Recognize Post-Translational Glycosylations on Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor Years Before Diagnosis and Predict Complicated Crohn's Disease
- PMID: 35623454
- PMCID: PMC10127946
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.05.029
Neutralizing Anti-Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor Autoantibodies Recognize Post-Translational Glycosylations on Granulocyte Macrophage-Colony Stimulating Factor Years Before Diagnosis and Predict Complicated Crohn's Disease
Abstract
Background & aims: Anti-granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor autoantibodies (aGMAbs) are detected in patients with ileal Crohn's disease (CD). Their induction and mode of action during or before disease are not well understood. We aimed to investigate the underlying mechanisms associated with aGMAb induction, from functional orientation to recognized epitopes, for their impact on intestinal immune homeostasis and use as a predictive biomarker for complicated CD.
Methods: We characterized using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay naturally occurring aGMAbs in longitudinal serum samples from patients archived before the diagnosis of CD (n = 220) as well as from 400 healthy individuals (matched controls) as part of the US Defense Medical Surveillance System. We used biochemical, cellular, and transcriptional analysis to uncover a mechanism that governs the impaired immune balance in CD mucosa after diagnosis.
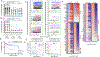
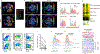
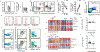
Results: Neutralizing aGMAbs were found to be specific for post-translational glycosylation on granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), detectable years before diagnosis, and associated with complicated CD at presentation. Glycosylation of GM-CSF was altered in patients with CD, and aGMAb affected myeloid homeostasis and promoted group 1 innate lymphoid cells. Perturbations in immune homeostasis preceded the diagnosis in the serum of patients with CD presenting with aGMAb and were detectable in the noninflamed CD mucosa.
Conclusions: Anti-GMAbs predict the diagnosis of complicated CD long before the diagnosis of disease, recognize uniquely glycosylated epitopes, and impair myeloid cell and innate lymphoid cell balance associated with altered intestinal immune homeostasis.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; Crohn’s Disease; GM-CSF; Innate Lymphoid Cells; Macrophages.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The University of Toronto and the Mount Sinai Hospital have collectively filed a patent application listing S.G., A.M., J.F.C., M.M., and R.R. as inventors, which is related in part to this publication. S.G. reports past consultancy and/or advisory roles for Merck and OncoMed and research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen R&D, Pfizer, Takeda, Boehringer-Ingelheim, and Regeneron. J.F.C. reports receiving research grants from AbbVie, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Takeda; receiving payment for lectures from AbbVie, Amgen, Allergan, Inc., Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Shire, and Takeda; receiving consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Eli Lilly, Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Galmed Research, Genentech, Glaxo Smith Kline, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Kaleido Biosciences, Imedex, Immunic, Iterative Scopes, Merck, Microba, Novartis, PBM Capital, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, TiGenix, Vifor; and holding stock options in Intestinal Biotech Development. C.K.P. is an employee of the US Government. This work was prepared as part of his official duties. Title 17 U.S.C. §105 provides that “Copyright protection under this title is not available for any work of the United States Government.” Title 17 U.S.C. §101 defines a US Government work as a work prepared by a military service member or employee of the US Government as part of that person’s official duties. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, nor the US Government. This is a US Government work. There are no restrictions on its use.
Figures
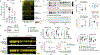
References
-
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2018;390:2769–2778. - PubMed
-
- Ananthakrishnan AN, Bernstein CN, Iliopoulos D, et al. Environmental triggers in IBD: a review of progress and evidence. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2018;15:39–49. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg MS, Satsangi J, Ahmad T, et al. Toward an integrated clinical, molecular and serological classification of inflammatory bowel disease: report of a Working Party of the 2005 Montreal World Congress of Gastroenterology. Can J Gastroenterol 2005;19(Suppl A):5A–36A. - PubMed
-
- Verhelst X, Dias AM, Colombel JF, et al. Protein glycosylation as a diagnostic and prognostic marker of chronic inflammatory gastrointestinal and liver diseases. Gastroenterology 2020;158:95–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

