Temporal regulation of neural diversity in Drosophila and vertebrates
- PMID: 35623984
- PMCID: PMC11585012
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.05.011
Temporal regulation of neural diversity in Drosophila and vertebrates
Abstract
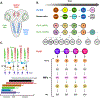
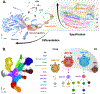
The generation of neuronal diversity involves temporal patterning mechanisms by which a given progenitor sequentially produces multiple cell types. Several parallels are evident between the brain development programs of Drosophila and vertebrates, such as the successive emergence of specific cell types and the use of combinations of transcription factors to specify cell fates. Furthermore, cell-extrinsic cues such as hormones and signaling pathways have also been shown to be regulatory modules of temporal patterning. Recently, transcriptomic and epigenomic studies using large single-cell sequencing datasets have provided insights into the transcriptional dynamics of neurogenesis in the Drosophila and mammalian central nervous systems. We review these commonalities in the specification of neuronal identity and highlight the conserved or convergent strategies of brain development by discussing temporal patterning mechanisms found in flies and vertebrates.
Keywords: Cell identity; Drosophila; Fate specification; Neuronal diversity; Temporal patterning; Vertebrates.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest None.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

