The HSP90 inhibitor KW-2478 depletes the malignancy of BCR/ABL and overcomes the imatinib-resistance caused by BCR/ABL amplification
- PMID: 35624462
- PMCID: PMC9137153
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-022-00287-w
The HSP90 inhibitor KW-2478 depletes the malignancy of BCR/ABL and overcomes the imatinib-resistance caused by BCR/ABL amplification
Abstract
Background: With the widespread clinical application of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), an increasing number of chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) patients have developed resistance or intolerance to TKIs. BCR/ABL is the oncoprotein of CML. HSP90 is an essential chaperone of BCR/ABL and plays an important role in protein folding and the function of BCR/ABL. Therefore, inhibiting the chaperone function of HSP90 may be an effective strategy for CML treatment and to overcome TKI resistance.
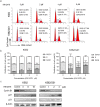
Methods: The effect of KW-2478 on CML cell viability, apoptosis and cell cycle progression was detected by CCK-8 assay or flow cytometry. The levels of BCR/ABL, HSP90 and other signalling proteins were detected by western blots. The mitochondrial membrane potential was detected by flow cytometry combined with JC-1 staining. The interaction between BCR/ABL and HSP90α was detected by coimmunoprecipitation. The effect of KW-2478 on BCR/ABL carcinogenesis in vivo was investigated in CML-like mouse models.
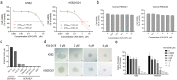
Results: KW-2478 inhibited growth and induced apoptosis of CML cells. KW-2478 inhibited the chaperone function of HSP90α and then weakened the BCR/ABL and MAPK signalling pathways. This treatment also caused an increase in p27 and p21 expression and a decrease in cyclin B1 expression, which led to G2/M phase arrest. The mitochondrial pathway was primarily responsible for KW-2478-induced apoptosis. KW-2478 had a synergistic effect with imatinib in growth inhibition. Notably, KW-2478 had a stronger effect on growth inhibition, apoptosis induction and cell cycle arrest of K562/G01 cells than K562 cells. KW-2478 could effectively prolong the mouse lifespan and alleviate disease symptoms in CML-like mouse models.
Conclusions: This finding demonstrated that KW-2478 had anticancer properties in imatinib-sensitive and imatinib-resistant CML cells and illustrated the possible mechanisms. This study provides an alternative choice for CML treatment, especially for TKI-resistant patients with BCR/ABL amplification and TKI-intolerant patients.
Keywords: BCR/ABL; HSP90 inhibitor; Imatinib resistance; KW-2478; Malignancy.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Dual inhibition of Bcr-Abl and Hsp90 by C086 potently inhibits the proliferation of imatinib-resistant CML cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Feb 15;21(4):833-43. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3317. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25501124
-
Targeting Hedgehog signaling pathway and autophagy overcomes drug resistance of BCR-ABL-positive chronic myeloid leukemia.Autophagy. 2015;11(2):355-72. doi: 10.4161/15548627.2014.994368. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25701353 Free PMC article.
-
A novel tubulin polymerization inhibitor, MPT0B206, downregulates Bcr-Abl expression and induces apoptosis in imatinib-sensitive and imatinib-resistant CML cells.Apoptosis. 2016 Sep;21(9):1008-18. doi: 10.1007/s10495-016-1264-z. Apoptosis. 2016. PMID: 27344662
-
Characterization of cancer stem cells in chronic myeloid leukaemia.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Nov;35(Pt 5):1347-51. doi: 10.1042/BST0351347. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17956348 Review.
-
[MET/ERK and MET/JNK Pathway Activation Is Involved in BCR-ABL Inhibitor-resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(12):1461-1466. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00142. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 30504658 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Hsp90α and cell death in cancers: a review.Discov Oncol. 2024 May 10;15(1):151. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01021-0. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38727789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chiglitazar diminishes the warburg effect through PPARγ/mTOR/PKM2 and increases the sensitivity of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Dec 18;13(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00589-1. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39696470 Free PMC article.
-
Co-targeting HSP90 alpha and CDK7 overcomes resistance against HSP90 inhibitors in BCR-ABL1+ leukemia cells.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Dec 6;14(12):799. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06337-3. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 38057328 Free PMC article.
-
AHSA1-HSP90AA1 complex stabilized IFI6 and TGFB1 promotes mitochondrial stability and EMT in EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma under Osimertinib pressure.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Apr 15;16(1):298. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07650-9. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40234395 Free PMC article.
-
Alvespimycin Inhibits Heat Shock Protein 90 and Overcomes Imatinib Resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines.Molecules. 2023 Jan 26;28(3):1210. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031210. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36770876 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

