Compact Microfluidic Platform with LED Light-Actuated Valves for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Automation
- PMID: 35624581
- PMCID: PMC9139117
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12050280
Compact Microfluidic Platform with LED Light-Actuated Valves for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay Automation
Abstract
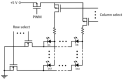
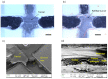
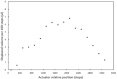
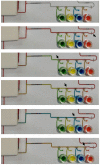
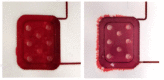
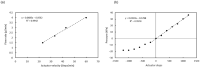
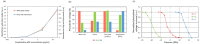
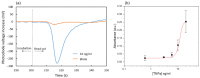
Lab-on-a-chip devices incorporating valves and pumps can perform complex assays involving multiple reagents. However, the instruments used to drive these chips are complex and bulky. In this article, a new wax valve design that uses light from a light emitting diode (LED) for both opening and closing is reported. The valves and a pumping chamber are integrated in lab-on-a-foil chips that can be fabricated at low cost using rapid prototyping techniques. A chip for the implementation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) is designed. A porous nitrocellulose material is used for the immobilization of capture antibodies in the microchannel. A compact generic instrument with an array of 64 LEDs, a linear actuator to drive the pumping chamber, and absorbance detection for a colorimetric readout of the assay is also presented. Characterization of all the components and functionalities of the platform and the designed chip demonstrate their potential for assay automation.
Keywords: lab-on-a-chip; lab-on-a-foil; microfluidic ELISA; wax valve.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Chen D., Mauk M., Qiu X., Liu C., Kim J., Ramprasad S., Ongagna S., Abrams W.R., Malamud D., Corstjens P.L., et al. An integrated, self-contained microfluidic cassette for isolation, amplification, and detection of nucleic acids. Biomed. Microdevices. 2010;12:705–719. doi: 10.1007/s10544-010-9423-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

