Role of SARS-CoV-2 in Modifying Neurodegenerative Processes in Parkinson's Disease: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 35624923
- PMCID: PMC9139310
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci12050536
Role of SARS-CoV-2 in Modifying Neurodegenerative Processes in Parkinson's Disease: A Narrative Review
Abstract
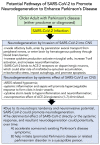
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by SARS-CoV-2, continues to impact global health regarding both morbidity and mortality. Although SARS-CoV-2 primarily causes acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), the virus interacts with and influences other organs and tissues, including blood vessel endothelium, heart, gastrointestinal tract, and brain. We are learning much about the pathophysiology of SARS-CoV-2 infection; however, we are just beginning to study and understand the long-term and chronic health consequences. Since the pandemic's beginning in late 2019, older adults, those with pre-existing illnesses, or both, have an increased risk of contracting COVID-19 and developing severe COVID-19. Furthermore, older adults are also more likely to develop the neurodegenerative disorder Parkinson's disease (PD), with advanced age as the most significant risk factor. Thus, does SARS-CoV-2 potentially influence, promote, or accelerate the development of PD in older adults? Our initial focus was aimed at understanding SARS-CoV-2 pathophysiology and the connection to neurodegenerative disorders. We then completed a literature review to assess the relationship between PD and COVID-19. We described potential molecular and cellular pathways that indicate dopaminergic neurons are susceptible, both directly and indirectly, to SARS-CoV-2 infection. We concluded that under certain pathological circumstances, in vulnerable persons-with-Parkinson's disease (PwP), SARS-CoV-2 acts as a neurodegenerative enhancer to potentially support the development or progression of PD and its related motor and non-motor symptoms.
Keywords: COVID-19; Parkinson’s disease; SARS-CoV-2; alpha-synuclein; angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor; brain; neurodegenerative disorder; neuroinflammation; older adults.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chen H., Guo J., Wang C., Luo F., Yu X., Zhang W., Li J., Zhao D., Xu D., Gong Q. Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: A retrospective review of medical records. Lancet. 2020;395:809–815. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30360-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

