Comparison of the Modified TyG Indices and Other Parameters to Predict Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Youth
- PMID: 35625413
- PMCID: PMC9138077
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11050685
Comparison of the Modified TyG Indices and Other Parameters to Predict Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Youth
Abstract
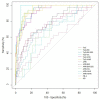
We investigated the modified triglycerides-glucose (TyG) indices and other markers for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in 225 participants aged 10-19 years, and the participants were divided into subgroups according to their NAFLD grade. We performed logistic regression analysis and calculated the odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of tertiles 2 and 3 for each parameter, with those of tertile 1 as a reference. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was calculated to compare the parameters for identifying NAFLD. TyG and modified indices, aspartate transaminase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI)-body mass index (BMI), APRI-BMI standard deviation score (SDS), APRI waist-to-hip ratio, fibrosis-4 index (FIB)-4, and hepatic steatosis index (HSI) were higher in participants with NAFLD than in those without NAFLD. The ORs and 95% CIs for NAFLD progressively increased across tertiles of each parameter. TyG and modified TyG indices, FIB-4, HSI, and modified APRIs, except APRI waist-to-height ratio, predicted NAFLD significantly through ROC curves. Modified TyG indices, APRI-BMI SDS, and HSI were superior to the other markers for NAFLD prediction. Modified TyG indices, APRI-BMI SDS, and HSI appear to be useful for assessing NAFLD in youths.
Keywords: adolescent; biomarkers; child; glucose; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Song K., Park G., Lee H.S., Lee M., Lee H.I., Ahn J., Lee E., Choi H.S., Suh J., Kwon A. Trends in prediabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated with abdominal obesity among korean children and adolescents: Based on the korea national health and nutrition examination survey between 2009 and 2018. Biomedicines. 2022;10:584. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10030584. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Song K., Park G., Lee H.S., Lee M., Lee H.I., Choi H.S., Suh J., Kwon A., Kim H.S., Chae H.W. Comparison of the triglyceride glucose index and modified triglyceride glucose indices to predict nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in youths. J. Pediatr. 2022;242:79–85.e71. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2021.11.042. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vos M.B., Abrams S.H., Barlow S.E., Caprio S., Daniels S.R., Kohli R., Mouzaki M., Sathya P., Schwimmer J.B., Sundaram S.S., et al. Naspghan clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: Recommendations from the expert committee on nafld (econ) and the north american society of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition (naspghan) J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017;64:319–334. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

